SARS-CoV-2 turned positive in a discharged patient with COVID-19 arouses concern regarding the present standards for discharge
- PMID: 32200109
- PMCID: PMC7270599
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijid.2020.03.007
SARS-CoV-2 turned positive in a discharged patient with COVID-19 arouses concern regarding the present standards for discharge
Abstract
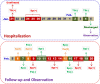
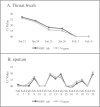
An outbreak of coronavirus disease (COVID-19) in Wuhan, China caused by SARS-CoV-2 has led to a serious epidemic in China and other countries, resulting in worldwide concern. With active efforts of prevention and control, more and more patients are being discharged. However, how to manage these patients normatively is still challenging. This paper reports an asymptomatic discharged patient with COVID-19 who retested positive for SARS-CoV-2, which arouses concern regarding the present discharge standards of COVID-19.
Keywords: COVID-19; Discharge standard; Turn positive.
Copyright © 2020 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures
Comment in
-
Patients with COVID-19: are current isolation guidelines effective enough?Public Health. 2020 Jun;183:38-39. doi: 10.1016/j.puhe.2020.04.048. Epub 2020 May 11. Public Health. 2020. PMID: 32417566 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Clinical management of severe acute respiratory infection when novel coronavirus . 2020. (2019-nCoV) infection is suspected Interim guidance. 28 January.https://www.who.int/publications-detail/clinical-management-of-severe-ac...
-
- Laboratory testing . 2020. Laboratory testing for 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) in suspected human cases Interim guidance. 17 January.https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/technica...
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

