Comparison of midazolam and low-dose dexmedetomidine in flexible bronchoscopy: A prospective, randomized, double-blinded study
- PMID: 32201443
- PMCID: PMC7074428
- DOI: 10.4103/ijp.IJP_287_19
Comparison of midazolam and low-dose dexmedetomidine in flexible bronchoscopy: A prospective, randomized, double-blinded study
Abstract
Background: Dexmedetomidine is a clinically useful drug for providing sedation, but concern regarding its cardiovascular side effect profile can limit its widespread use during routine diagnostic flexible bronchoscopy (FB).
Materials and methods: Patients between 18 and 65 years of age, who required diagnostic FB, were screened. Eligible patients were randomized to either receive 0.5 μg/kg intravenous dexmedetomidine over 10 min or intravenous midazolam 0.035 mg/kg over 1 min. If required, rescue medication (intravenous midazolam 0.5 mg bolus) was administered. The primary outcome measure was the composite score. Other parameters observed were numerical rating scale, hemodynamic variables, oxygen saturation, number of doses of rescue medication, visual analog scale score for cough, ease of bronchoscopy, Ramsay Sedation Score, and postprocedure patient response after 24 h of bronchoscopy.
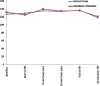
Results: A total of 54 patients were enrolled, 27 in each group. Total composite score (mean ± standard deviation) in dexmedetomidine and midazolam group at nasopharynx was 7.04 ± 2.19 and 6.59 ± 1.55 (P = 0.387), respectively. The corresponding values at the level of trachea were 9.22 ± 3.69 and 8.63 ± 2.13 (P = 0.475). In the dexmedetomidine group, patient response after 24 h of bronchoscopy showed the quality of sedation to be excellent in three patients, good in 10, fair in 11, and poor in 3 and discomfort to be nil in 14, mild 7, moderate in 3, and severe in 3. The corresponding values in the midazolam group for the quality of sedation were 0, 9, 18, 0 and for discomfort 10, 16, 1, 0. Other parameters did not reveal any statistically significant difference.
Conclusion: Dexmedetomidine at a dose of 0.5 μg/kg may provide clinically useful conscious sedation, comparable to midazolam.
Keywords: Dexmedetomidine; flexible bronchoscopy; midazolam; sedation.
Copyright: © 2020 Indian Journal of Pharmacology.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Du Rand IA, Blaikley J, Booton R, Chaudhuri N, Gupta V, Khalid S, et al. British Thoracic Society guideline for diagnostic flexible bronchoscopy in adults: Accredited by NICE. Thorax. 2013;68(Suppl 1):i1–44. - PubMed
-
- Barnett AM, Jones R, Simpson G. A survey of bronchoscopy practice in Australia and New Zealand. J Bronchology Interv Pulmonol. 2016;23:22–8. - PubMed
-
- Hwang J, Jeon Y, Park HP, Lim YJ, Oh YS. Comparison of alfetanil and ketamine in combination with propofol for patient-controlled sedation during fiberoptic bronchoscopy. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2005;49:1334–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources