Serum Endocan Levels Predict Drug-Eluting Stent Restenosis in Patients with Stable Angina Pectoris
- PMID: 32201461
- PMCID: PMC7062819
- DOI: 10.6515/ACS.202003_36(2).20190731A
Serum Endocan Levels Predict Drug-Eluting Stent Restenosis in Patients with Stable Angina Pectoris
Abstract
Background: Endothelial cell-specific molecule 1 (ESM-1 or endocan) is an immunoinflammatory marker strongly associated with inflammation, vascular endothelial dysfunction and atherosclerosis. We explored the relationship between serum endocan concentrations and coronary in-stent restenosis (ISR).
Methods: Fifty consecutive patients with ISR and 50 control subjects were included in this study. Clinical data and angiographic characteristics were collected. Serum endocan concentrations were measured using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.
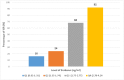
Results: All included patients were divided into four quartiles based on their concentrations of endocan: quartile 1 (0.62-1.31 ng/mL), quartile 2 (1.33-1.74 ng/mL), quartile 3 (1.75-2.77 ng/mL) and quartile 4 (2.78-4.24 ng/mL). The rates of ISR were 16%, 24%, 68%, and 92%, respectively. The patients in quartile 4 had significantly higher rates of ISR than the other groups (p < 0.001). Logistic regression analysis indicated that endocan concentration [odds ratio = 8.65, 95% confidence interval 3.56-20.94; p < 0.001] was an independent predictor of ISR. Receiver operating characteristic curve analysis was used to explore the relationship between endocan and ISR. Using a cutoff value of 1.625 ng/mL, endocan predicted ISR with a sensitivity of 86% and a specificity of 78%.
Conclusions: Our findings suggest that plasma endocan levels may be a novel biomarker of endothelial dysfunction in patients with ISR.
Keywords: Biomarker; Endocan; Endothelial cell-specific molecule 1; Inflammation.
Figures
References
-
- Patel MJ, Patel SS, Patel NS, Patel NM. Current status and future prospects of drug eluting stents for restenosis. Acta Pharma. 2012;62:473–476. - PubMed
-
- Paudel B, Xuan GJ, Chun ZF. Analysis of clinical factors affecting the restenosis following percutaneous coronary intervention. Nepal Med Coll J. 2005;7:101–106. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources