miR-23a-3p/SIX1 regulates glucose uptake and proliferation through GLUT3 in head and neck squamous cell carcinomas
- PMID: 32201523
- PMCID: PMC7066005
- DOI: 10.7150/jca.30995
miR-23a-3p/SIX1 regulates glucose uptake and proliferation through GLUT3 in head and neck squamous cell carcinomas
Abstract
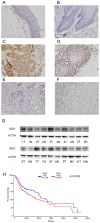
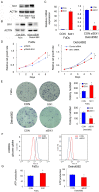
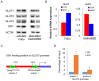
SIX1 overexpression has been reported in several cancers. However, its involvement in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) remains unclear. In this study we investigated the clinical significance and biological roles of SIX1 in HNSCC. SIX1 expression was upregulated in HNSCC and correlated with TNM stage and nodal metastasis. Analysis of TCGA dataset demonstrated that high SIX1 expression correlated with poor patient prognosis. Overexpression of SIX1 in the Fadu cell line upregulated cell proliferation, colony formation, glucose uptake and ATP production. In contrast, SIX1 depletion in the Detroit562 cell line downregulated cell proliferation, colony formation, glucose uptake and ATP production. We analyzed a series of genes involved in glucose metabolism and found that SIX1 overexpression upregulated GLUT3, an important glucose transporter, at both mRNA and protein levels. Using the TRANSFAC database, we found that SIX1 had potential binding sites on the GLUT3 promoter, which was validated by chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) assays. Next, we focused on miR-23a-3p, which could target SIX1 in HNSCC cells. The miR-23a-3p mimic downregulated SIX1 expression while the miR-23a-3p inhibitor upregulated SIX1 expression. The binding of miR-23a-3p to the 3'-UTR of SIX1 was confirmed using the luciferase reporter assay. Analysis of TCGA dataset showed a negative correlation between the miR-23a-3p and SIX1. Furthermore, the miR-23a-3p mimic inhibited cell proliferation, ATP production and glucose uptake, which could be rescued by transfection with the SIX1 plasmid. In summary, our study demonstrated that SIX1 facilitated HNSCC cell growth through regulation of GLUT3 and glucose uptake. miR-23a-3p targeted the SIX1/GLUT3 axis and suppressed glucose uptake and proliferation in HNSCC.
Keywords: GLUT3; SIX1; glucose metabolism; head and neck squamous cell carcinoma; miR-23a-3p.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Six1 Overexpression Promotes Glucose Metabolism and Invasion Through Regulation of GLUT3, MMP2 and Snail in Thyroid Cancer Cells.Onco Targets Ther. 2020 May 29;13:4855-4863. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S227291. eCollection 2020. Onco Targets Ther. 2020. PMID: 32581547 Free PMC article.
-
miR-489-3p/SIX1 Axis Regulates Melanoma Proliferation and Glycolytic Potential.Mol Ther Oncolytics. 2019 Nov 27;16:30-40. doi: 10.1016/j.omto.2019.11.001. eCollection 2020 Mar 27. Mol Ther Oncolytics. 2019. PMID: 32258386 Free PMC article.
-
miR-23a-3p suppresses cell proliferation in oral squamous cell carcinomas by targeting FGF2 and correlates with a better prognosis: miR-23a-3p inhibits OSCC growth by targeting FGF2.Pathol Res Pract. 2019 Apr;215(4):660-667. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2018.12.021. Epub 2018 Dec 24. Pathol Res Pract. 2019. PMID: 30606659
-
Overexpression of TRIM24 Stimulates Proliferation and Glucose Metabolism of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Biomed Res Int. 2018 May 10;2018:6142843. doi: 10.1155/2018/6142843. eCollection 2018. Biomed Res Int. 2018. PMID: 29862279 Free PMC article.
-
Antitumor miR-150-5p and miR-150-3p inhibit cancer cell aggressiveness by targeting SPOCK1 in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Auris Nasus Larynx. 2018 Aug;45(4):854-865. doi: 10.1016/j.anl.2017.11.019. Epub 2017 Dec 9. Auris Nasus Larynx. 2018. PMID: 29233721
Cited by
-
SIX1 enhances aerobic glycolysis and progression in cervical cancer through ENO1.Hum Cell. 2025 Apr 15;38(3):88. doi: 10.1007/s13577-025-01215-w. Hum Cell. 2025. PMID: 40234326
-
Inhibition of lncRNA NEAT1 sensitizes medulloblastoma cells to cisplatin through modulating the miR-23a-3p-glutaminase (GLS) axis.Bioengineered. 2022 Mar;13(3):7670-7682. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.2008695. Bioengineered. 2022. PMID: 35313796 Free PMC article.
-
Tanshinone IIA inhibits cell growth by suppressing SIX1-induced aerobic glycolysis in non-small cell lung cancer cells.Oncol Lett. 2022 Jun;23(6):184. doi: 10.3892/ol.2022.13304. Epub 2022 Apr 21. Oncol Lett. 2022. PMID: 35527783 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional regulation and post-translational modifications in the glycolytic pathway for targeted cancer therapy.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2024 Aug;45(8):1533-1555. doi: 10.1038/s41401-024-01264-1. Epub 2024 Apr 15. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2024. PMID: 38622288 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of the Dysregulation of Long Non-Coding and Circular RNA Expression in Medulloblastoma: A Systematic Review.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Sep 22;15(19):4686. doi: 10.3390/cancers15194686. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37835380 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Leemans CR, Braakhuis BJ, Brakenhoff RH. The molecular biology of head and neck cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2011;11:9–22. - PubMed
-
- Chow LQM, Haddad R, Gupta S, Mahipal A, Mehra R, Tahara M. et al. Antitumor Activity of Pembrolizumab in Biomarker-Unselected Patients With Recurrent and/or Metastatic Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Results From the Phase Ib KEYNOTE-012 Expansion Cohort. J Clin Oncol. 2016;34:3838–45. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lu J, Getz G, Miska EA, Alvarez-Saavedra E, Lamb J, Peck D. et al. MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature. 2005;435:834–8. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

