MicroRNA-145 suppresses epithelial to mesenchymal transition in pancreatic cancer cells by inhibiting TGF-β signaling pathway
- PMID: 32201542
- PMCID: PMC7066001
- DOI: 10.7150/jca.34902
MicroRNA-145 suppresses epithelial to mesenchymal transition in pancreatic cancer cells by inhibiting TGF-β signaling pathway
Abstract
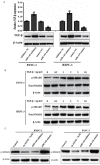
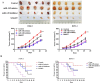
TGF-β signaling plays a critical role in tumor progression and many approaches have been made to inhibit its functions. MicroRNA is one of the approaches that inhibit TGF-β signaling and can be used as a promising treatment for cancer. This study explored the role of miRNA-145 in pancreatic cancer (PC) development. The expression of miRNA-145 in PC tissues and paired adjacent normal tissues was examined by qRT-PCR. The expression of miRNA-145 in PC cells and the ability of cell migration and invasion were detected both in vivo and in vitro. The results showed that miRNA-145 was down-regulated in PC tissues and PC cells. Increasing the expression of miRNA-145 in PC cells inhibited the TGF-β signaling pathway and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) process. Scratch assay and transwell assay showed that miRNA-145 inhibited the migration and invasion in PC cells. In vivo experiments confirmed that miRNA-145 mimics delayed the growth of PC xenografts comparing with miRNA-145 inhibitor. Our results suggested that miRNA-145 can inhibit epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT) and tumor growth by suppressing TGF-β signaling pathway. Thus, miRNA-145 could be a potential therapeutic for targeting TGF-β signaling in PC treatment.
Keywords: EMT; TGF- β signaling; metastasis; miRNA-145; pancreatic cancer.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures



References
-
- Malvezzi M, Carioli G, Bertuccio P, Rosso T, Boffetta P, Levi F. et al. European cancer mortality predictions for the year 2016 with focus on leukaemias. Ann Oncol. 2016;27:725–31. - PubMed
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer Statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin. 2017;67:7–30. - PubMed
-
- Farazi TA, Juranek SA, Tuschl T. The growing catalog of small RNAs and their association with distinct Argonaute/Piwi family members. Development. 2008;135:1201–14. - PubMed
-
- Croce CM, Calin GA. miRNAs, cancer, and stem cell division. Cell. 2005;122:6–7. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

