Ending TB in Southeast Asia: current resources are not enough
- PMID: 32201625
- PMCID: PMC7059409
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjgh-2019-002073
Ending TB in Southeast Asia: current resources are not enough
Abstract
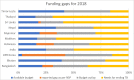
The Southeast Asia Region continues to battle tuberculosis (TB) as one of its most severe health and development challenges. Unless there is a substantial increase in investments for TB prevention, diagnosis, care and treatment, there will be catastrophic effects for the region. The uncontrolled TB burden impacts socioeconomic development and increase of drug resistance in the region. Based on epidemiological inputs from a mathematical model, a costing analysis estimates that the desired targets of ending TB are achievable with additional interventions, and critical thresholds require an increase in spending by almost double the current levels. The data source for financial allocation to TB programmes is the report submitted by countries to WHO, while projections are based on modelling. The model accounts for funding needs for all strategies based on published data and accounts for programme and patient costs. This paper delineates the resource needs, availability and gaps of ending TB in the region. It is estimated that close to US$2 billion per year are needed in the region for TB-related activities for a meaningful bending of the incidence curve towards ending TB.
Keywords: end TB targets; resource needs; southeast Asia region; tuberculosis.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2020. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
References
-
- WHO Global tuberculosis report 2019. Global tuberculosis report, 2019.
-
- WHO SEARO Ending TB: invest now or pay later, 2018.
-
- WHO Global tuberculosis report 2018. World Health Organization, 2018.
-
- IHME Findings from the global burden of disease study 2017. Seattle, WA: IHME, 2018.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical