Comparative proteinuria management of different angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers for normotensive patients with CKD: a Bayesian network meta-analysis
- PMID: 32201639
- PMCID: PMC7073241
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.8575
Comparative proteinuria management of different angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers for normotensive patients with CKD: a Bayesian network meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Both angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEIs) and angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs) are blood pressure-lowering agents, but they are also being used to control proteinuria in early chronic kidney disease (CKD) patients. However, clinically, some patients present merely proteinuria without hypertension. No guidelines pointed out how to select treatments for proteinuria in normotensive patients. Thus, we conducted a Bayesian network analysis to evaluate the relative effects of different kinds of ACEI or ARB or their combination on proteinuria and blood pressure reduction.
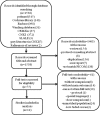
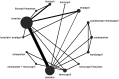
Methods: The protocol was registered in PROSPERO with ID CRD42017073721. A comprehensive literature database query was carried out systematically according to PICOS strategies. The primary outcome was reduction in proteinuria, and the secondary outcomes were eGFR reduction and blood pressure reduction. Random-effects pairwise and Bayesian network meta-analyses were used to estimate the effect of different regimens.
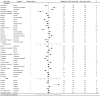
Results: A total of 14 RCTs with 1,098 patients were included in the analysis. All treatment strategies of ACEI, ARB or their combination had significantly greater efficacy in reducing proteinuria than placebo in normotensive CKD patients. The combination therapy of olmesartan+temocapril had the highest probability (22%) of being the most effective treatment to reduce proteinuria in normotensive CKD patients. Olmesartan and lisinopril ranked second (12%), and temocapril ranked third (15%) but reduced blood pressure less than placebo. For IgA nephropathy, the combination therapy of olmesartan+temocapril also had the highest probability (43%) of being the best antiproteinuric treatment, while enalapril had the highest probability (58%) of being the best antiproteinuric therapy for diabetic nephropathy.
Conclusions: The combination therapy of olmesartan plus temocapril appeared to be the most efficacious for reducing proteinuria in normotensive CKD patients and IgA nephropathy, but the clinical application should be balanced against potential harms. Temocapril can be an option when practitioners are searching for more proteinuria reduction but less blood pressure variation. In normotensive diabetic nephropathy, monotherapy with the ACEI enalapril seems to be the most efficacious intervention for reducing albuminuria. Future studies are required to give a more definitive recommendation.
Keywords: ARB; ACEI; Bayesian network analysis.; Chronic kidney disease; Normotension; Proteinuria reduction.
©2020 Ye et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare there are no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Agha A, Amer W, Anwar E, Bashir K. Reduction of microalbuminuria by using losartan in normotensive patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a randomized controlled trial. Saudi Journal of Kidney Diseases and Transplantation. 2009;20:429–435. - PubMed
-
- Chen PM, Wada T, Chiang CK. Prognostic value of proteinuria and glomerular filtration rate on Taiwanese patients with diabetes mellitus and advanced chronic kidney disease: a single center experience. Clinical and Experimental Nephrology. 2017;21:307–315. doi: 10.1007/s10157-016-1290-8. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous