Real-world assay variability between laboratories in monitoring of recombinant factor IX Fc fusion protein activity in plasma samples
- PMID: 32202380
- PMCID: PMC7318191
- DOI: 10.1111/ijlh.13189
Real-world assay variability between laboratories in monitoring of recombinant factor IX Fc fusion protein activity in plasma samples
Abstract
Introduction: Monitoring of factor IX (FIX) replacement therapy in haemophilia B relies on accurate coagulation assays. However, considerable interlaboratory variability has been reported for one-stage clotting (OSC) assays. This study aimed to evaluate the real-world, interlaboratory variability of routine FIX activity assays used in clinical haemostasis laboratories for the measurement of recombinant FIX Fc fusion protein (rFIXFc) activity.
Methods: Human FIX-depleted plasma was spiked with rFIXFc at 0.80, 0.20 or 0.05 IU/mL based on label potency. Participating laboratories tested samples using their own routine OSC or chromogenic substrate (CS) assay protocols, reagents and FIX plasma standards. Laboratories could perform more than one measurement and method, and were not fully blinded to nominal activity values.
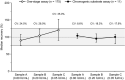
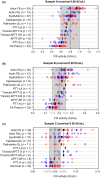
Results: A total of 142 laboratories contributed OSC results from 175 sample kits using 11 different activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT) reagents. The median recovered FIX activity for the 0.80, 0.20 and 0.05 IU/mL samples was 0.72 IU/mL, 0.21 IU/mL and 0.060 IU/mL, respectively. Across all OSC reagents, interlaboratory variability (% CV) per aPTT reagent ranged from 9.4% to 32.1%, 8.2% to 32.6% and 12.2% to 42.0% at the 0.80, 0.20 and 0.05 IU/mL levels, respectively. CS results showed excellent median recoveries at all nominal levels (87.5% to 115.0%; n = 11) with low interlaboratory variability (CV 3.6% to 15.4%).
Conclusion: This large, real-world data set indicates that rFIXFc activity in plasma samples can be accurately measured with the majority of routine OSC and CS assay methods. Given the variation in FIX assay procedures between sites, it is important that individual laboratories qualify their in-house methods for monitoring of rFIXFc activity.
Keywords: chromogenic substrate assay; factor IX replacement therapy; haemophilia B; one-stage clotting assay; recombinant factor IX Fc fusion protein.
© 2020 Swedish Orphan Biovitrum AB. International Journal of Laboratory Hematology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
JS: Employee of Biogen at the time of the study; consultancy fees from Sobi; ASK: Employee of Precision BioLogic; CB: Employee of Sanofi Genzyme; MW: Employee of Sobi at the time of the study; AW: Employee of Sobi at the time of the study; current employee of Sanofi.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparative field study: impact of laboratory assay variability on the assessment of recombinant factor IX Fc fusion protein (rFIXFc) activity.Thromb Haemost. 2014 Nov;112(5):932-40. doi: 10.1160/TH13-11-0971. Epub 2014 Aug 21. Thromb Haemost. 2014. PMID: 25144892 Free PMC article.
-
Performance of a recombinant fusion protein linking coagulation factor IX with recombinant albumin in one-stage clotting assays.J Thromb Haemost. 2019 Jan;17(1):138-148. doi: 10.1111/jth.14332. Epub 2018 Dec 16. J Thromb Haemost. 2019. PMID: 30418692 Free PMC article.
-
Recombinant FIX Fc fusion protein activity assessment with the one-stage clotting assay: A multicenter, assessor-blinded, prospective study in Japan (J-Field Study).Int J Lab Hematol. 2020 Apr;42(2):162-169. doi: 10.1111/ijlh.13133. Epub 2019 Dec 10. Int J Lab Hematol. 2020. PMID: 31820573 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Factor VIII and IX assays for post-infusion monitoring in hemophilia patients: Guidelines from the French BIMHO group (GFHT).Eur J Haematol. 2020 Aug;105(2):103-115. doi: 10.1111/ejh.13423. Epub 2020 May 27. Eur J Haematol. 2020. PMID: 32277501 Review.
-
Continuous prophylaxis with recombinant factor IX Fc fusion protein and conventional recombinant factor IX products: comparisons of efficacy and weekly factor consumption.J Med Econ. 2017 Apr;20(4):337-344. doi: 10.1080/13696998.2016.1265973. Epub 2016 Dec 21. J Med Econ. 2017. PMID: 27885871
Cited by
-
An Update on Laboratory Diagnostics in Haemophilia A and B.Hamostaseologie. 2022 Aug;42(4):248-260. doi: 10.1055/a-1665-6232. Epub 2022 Feb 1. Hamostaseologie. 2022. PMID: 35104901 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recombinant factor IX Fc for major surgery in hemophilia B: factor IX plasma activity levels and effective hemostasis.Res Pract Thromb Haemost. 2023 Aug 7;7(6):102169. doi: 10.1016/j.rpth.2023.102169. eCollection 2023 Aug. Res Pract Thromb Haemost. 2023. PMID: 37694269 Free PMC article.
-
Global Comparative Antithrombin Field Study: Impact of Laboratory Assay Variability on the Assessment of Antithrombin Activity Measurement at Fitusiran Clinical Decision-Making Points.Haemophilia. 2025 May;31(3):566-574. doi: 10.1111/hae.70045. Epub 2025 Apr 20. Haemophilia. 2025. PMID: 40254822 Free PMC article.
-
Managing surgery in hemophilia with recombinant factor VIII Fc and factor IX Fc: Data on safety and effectiveness from phase 3 pivotal studies.Res Pract Thromb Haemost. 2022 Jul 26;6(5):e12760. doi: 10.1002/rth2.12760. eCollection 2022 Jul. Res Pract Thromb Haemost. 2022. PMID: 35910942 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Iorio A, Blanchette V, Blatny J, Collins P, Fischer K, Neufeld E. Estimating and interpreting the pharmacokinetic profiles of individual patients with hemophilia A or B using a population pharmacokinetic approach: communication from the SSC of the ISTH. J Thromb Haemost. 2017;15(12):2461‐2465. - PubMed
-
- Iorio A, Fischer K, Blanchette V, Rangarajan S, Young G, Morfini M. Tailoring treatment of haemophilia B: accounting for the distribution and clearance of standard and extended half‐life FIX concentrates. Thromb Haemost. 2017;117(6):1023‐1030. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

