A model for focal seizure onset, propagation, evolution, and progression
- PMID: 32202494
- PMCID: PMC7089769
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.50927
A model for focal seizure onset, propagation, evolution, and progression
Abstract
We developed a neural network model that can account for major elements common to human focal seizures. These include the tonic-clonic transition, slow advance of clinical semiology and corresponding seizure territory expansion, widespread EEG synchronization, and slowing of the ictal rhythm as the seizure approaches termination. These were reproduced by incorporating usage-dependent exhaustion of inhibition in an adaptive neural network that receives global feedback inhibition in addition to local recurrent projections. Our model proposes mechanisms that may underline common EEG seizure onset patterns and status epilepticus, and postulates a role for synaptic plasticity in the emergence of epileptic foci. Complex patterns of seizure activity and bi-stable seizure end-points arise when stochastic noise is included. With the rapid advancement of clinical and experimental tools, we believe that this model can provide a roadmap and potentially an in silico testbed for future explorations of seizure mechanisms and clinical therapies.
Keywords: EEG; computational biology; epilepsy; focal seizure; human; neuroscience; seizure models; synaptic plasticity; systems biology; traveling waves.
© 2020, Liou et al.
Conflict of interest statement
JL, ES, LB, SB, GM, RG, RE, CS, LA No competing interests declared
Figures

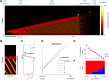



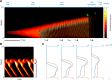
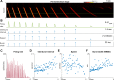







Comment in
-
Connecting Pathological Cellular Mechanisms to Large-Scale Seizure Structures.Trends Neurosci. 2020 Aug;43(8):547-549. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2020.04.006. Epub 2020 May 3. Trends Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32376035 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahmed OJ, Kramer MA, Truccolo W, Naftulin JS, Potter NS, Eskandar EN, Cosgrove GR, Blum AS, Hochberg LR, Cash SS. Inhibitory single neuron control of seizures and epileptic traveling waves in humans. BMC Neuroscience. 2014;15:F3. doi: 10.1186/1471-2202-15-S1-F3. - DOI
-
- Berens P. CircStat : a MATLAB toolbox for circular statistics. Journal of Statistical Software. 2009;31:1–21. doi: 10.18637/jss.v031.i10. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

