Risk of serious infection among individuals with and without low count monoclonal B-cell lymphocytosis (MBL)
- PMID: 32203143
- PMCID: PMC7501139
- DOI: 10.1038/s41375-020-0799-8
Risk of serious infection among individuals with and without low count monoclonal B-cell lymphocytosis (MBL)
Conflict of interest statement
Compliance with ethical standards
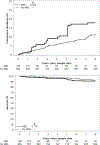
Figures
References
-
- Rawstron A, Green M, Kuzmicki A, Kennedy B, Fenton J, Evans P, et al. Monoclonal B lymphocytes with the characteristics of “indolent” chronic lymphocytic leukemia are present in 3.5% of adults with normal blood counts. Blood. 2002;100:635–9. - PubMed
-
- Moreira J, Rabe KG, Cerhan JR, Kay NE, Wilson JW, Call TG, et al. Infectious complications among individuals with clinical monoclonal B-cell lymphocytosis (MBL): a cohort study of newly diagnosed cases compared to controls. Leukemia. 2013;27:136–41. - PubMed
-
- Fazi C, Scarfo L, Pecciarini L, Cottini F, Dagklis A, Janus A, et al. General population low-count CLL-like MBL persists over time without clinical progression, although carrying the same cytogenetic abnormalities of CLL. Blood. 2011;118:6618–25. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

