Kcnn2 blockade reverses learning deficits in a mouse model of fetal alcohol spectrum disorders
- PMID: 32203497
- PMCID: PMC7131887
- DOI: 10.1038/s41593-020-0592-z
Kcnn2 blockade reverses learning deficits in a mouse model of fetal alcohol spectrum disorders
Abstract
Learning disabilities are hallmarks of congenital conditions caused by prenatal exposure to harmful agents. These include fetal alcohol spectrum disorders (FASDs) with a wide range of cognitive deficiencies, including impaired motor skill development. Although these effects have been well characterized, the molecular effects that bring about these behavioral consequences remain to be determined. We previously found that the acute molecular responses to alcohol in the embryonic brain are stochastic, varying among neural progenitor cells. However, the pathophysiological consequences stemming from these heterogeneous responses remain unknown. Here we show that acute responses to alcohol in progenitor cells altered gene expression in their descendant neurons. Among the altered genes, an increase of the calcium-activated potassium channel Kcnn2 in the motor cortex correlated with motor learning deficits in a mouse model of FASD. Pharmacologic blockade of Kcnn2 improves these learning deficits, suggesting Kcnn2 blockers as a new intervention for learning disabilities in FASD.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests Statement
K.H-T., M.T. and S.M. are founders of Cogthera LLC, a biotechnology company with a mission to develop SK2 blockers for neurocognitive disorders.
Figures
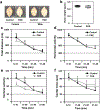
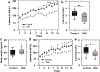
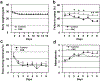
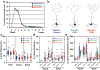
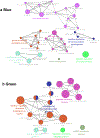
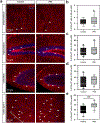
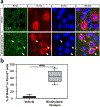
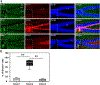

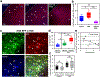

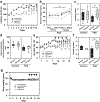
Comment in
-
Channel problems.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2020 Jun;21(6):300. doi: 10.1038/s41583-020-0305-3. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32286549 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Small-conductance Ca(2+)-activated K(+) channels: Heterogeneous affinity in rat brain structures and cognitive modulation by specific blockers.Eur J Pharmacol. 2008 Jul 28;589(1-3):140-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2008.05.019. Epub 2008 May 23. Eur J Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 18561910
-
SK channel blockade reverses cognitive and motor deficits induced by nigrostriatal dopamine lesions in rats.Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2014 Aug;17(8):1295-306. doi: 10.1017/S1461145714000236. Epub 2014 Mar 24. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24661728
-
Aversive Learning Deficits and Depressive-Like Behaviors Are Accompanied by an Increase in Oxidative Stress in a Rat Model of Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders: The Protective Effect of Rapamycin.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jun 30;22(13):7083. doi: 10.3390/ijms22137083. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34209274 Free PMC article.
-
Fetal alcohol syndrome: early olfactory learning as a model system to study neurobehavioral deficits.Int J Neurosci. 1997 Jan;89(1-2):119-32. doi: 10.3109/00207459708988467. Int J Neurosci. 1997. PMID: 9134450 Review.
-
Embryonic alcohol exposure: Towards the development of a zebrafish model of fetal alcohol spectrum disorders.Dev Psychobiol. 2015 Nov;57(7):787-98. doi: 10.1002/dev.21318. Epub 2015 Jun 16. Dev Psychobiol. 2015. PMID: 26079519 Review.
Cited by
-
Long-term spatial tracking of cells affected by environmental insults.J Neurodev Disord. 2020 Dec 16;12(1):38. doi: 10.1186/s11689-020-09339-w. J Neurodev Disord. 2020. PMID: 33327938 Free PMC article.
-
Gestational ethanol exposure impairs motor skills in female mice through dysregulated striatal dopamine and acetylcholine function.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2023 Nov;48(12):1808-1820. doi: 10.1038/s41386-023-01594-4. Epub 2023 May 15. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2023. PMID: 37188849 Free PMC article.
-
Reduction of APOE accounts for neurobehavioral deficits in fetal alcohol spectrum disorders.Mol Psychiatry. 2024 Nov;29(11):3364-3380. doi: 10.1038/s41380-024-02586-6. Epub 2024 May 11. Mol Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 38734844 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of the Novel Gene Markers Based on the Gene Profile among Different Severity of Obstructive Sleep Apnea.Comput Math Methods Med. 2022 Oct 4;2022:6517965. doi: 10.1155/2022/6517965. eCollection 2022. Comput Math Methods Med. 2022. PMID: 36245838 Free PMC article.
-
Sensory Motor Function Disturbances in Mice Prenatally Exposed to Low Dose of Ethanol: A Neurobehavioral Study in Postnatal and Adult Stages.Neurol Int. 2023 Apr 19;15(2):580-594. doi: 10.3390/neurolint15020036. Neurol Int. 2023. PMID: 37092508 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Grandjean P & Landrigan PJ Developmental neurotoxicity of industrial chemicals. Lancet 368, 2167–2178 (2006). - PubMed
-
- Diamond A & Lee EY Inability of five-month-old infants to retrieve a contiguous object: a failure of conceptual understanding or of control of action? Child Dev 71, 1477–1494 (2000). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

