Pemigatinib for previously treated, locally advanced or metastatic cholangiocarcinoma: a multicentre, open-label, phase 2 study
- PMID: 32203698
- PMCID: PMC8461541
- DOI: 10.1016/S1470-2045(20)30109-1
Pemigatinib for previously treated, locally advanced or metastatic cholangiocarcinoma: a multicentre, open-label, phase 2 study
Erratum in
-
Correction to Lancet Oncol 2020; 21: 671-84.Lancet Oncol. 2024 Jan;25(1):e3. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(23)00642-3. Lancet Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38181811 No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR) 2 gene alterations are involved in the pathogenesis of cholangiocarcinoma. Pemigatinib is a selective, potent, oral inhibitor of FGFR1, 2, and 3. This study evaluated the safety and antitumour activity of pemigatinib in patients with previously treated, locally advanced or metastatic cholangiocarcinoma with and without FGFR2 fusions or rearrangements.
Methods: In this multicentre, open-label, single-arm, multicohort, phase 2 study (FIGHT-202), patients aged 18 years or older with disease progression following at least one previous treatment and an Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance status of 0-2 recruited from 146 academic or community-based sites in the USA, Europe, the Middle East, and Asia were assigned to one of three cohorts: patients with FGFR2 fusions or rearrangements, patients with other FGF/FGFR alterations, or patients with no FGF/FGFR alterations. All enrolled patients received a starting dose of 13·5 mg oral pemigatinib once daily (21-day cycle; 2 weeks on, 1 week off) until disease progression, unacceptable toxicity, withdrawal of consent, or physician decision. The primary endpoint was the proportion of patients who achieved an objective response among those with FGFR2 fusions or rearrangements, assessed centrally in all patients who received at least one dose of pemigatinib. This study is registered with ClinicalTrials.gov, NCT02924376, and enrolment is completed.
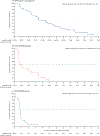
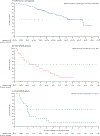
Findings: Between Jan 17, 2017, and March 22, 2019, 146 patients were enrolled: 107 with FGFR2 fusions or rearrangements, 20 with other FGF/FGFR alterations, 18 with no FGF/FGFR alterations, and one with an undetermined FGF/FGFR alteration. The median follow-up was 17·8 months (IQR 11·6-21·3). 38 (35·5% [95% CI 26·5-45·4]) patients with FGFR2 fusions or rearrangements achieved an objective response (three complete responses and 35 partial responses). Overall, hyperphosphataemia was the most common all-grade adverse event irrespective of cause (88 [60%] of 146 patients). 93 (64%) patients had a grade 3 or worse adverse event (irrespective of cause); the most frequent were hypophosphataemia (18 [12%]), arthralgia (nine [6%]), stomatitis (eight [5%]), hyponatraemia (eight [5%]), abdominal pain (seven [5%]), and fatigue (seven [5%]). 65 (45%) patients had serious adverse events; the most frequent were abdominal pain (seven [5%]), pyrexia (seven [5%]), cholangitis (five [3%]), and pleural effusion (five [3%]). Overall, 71 (49%) patients died during the study, most frequently because of disease progression (61 [42%]); no deaths were deemed to be treatment related.
Interpretation: These data support the therapeutic potential of pemigatinib in previously treated patients with cholangiocarcinoma who have FGFR2 fusions or rearrangements.
Funding: Incyte Corporation.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

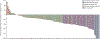
Comment in
-
Pemigatinib Is Active in Some FGFR2-Altered Cholangiocarcinomas.Cancer Discov. 2020 May;10(5):639. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-RW2020-050. Epub 2020 Apr 3. Cancer Discov. 2020. PMID: 32245820
-
Benefit from pemigatinib in cholangiocarcinoma.Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2020 Jun;17(6):337. doi: 10.1038/s41571-020-0369-z. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32300194 No abstract available.
References
-
- Babina IS, Turner NC. Advances and challenges in targeting FGFR signalling in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 2017; 17: 318–32. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

