Structural Variation of the X Chromosome Heterochromatin in the Anopheles gambiae Complex
- PMID: 32204543
- PMCID: PMC7140835
- DOI: 10.3390/genes11030327
Structural Variation of the X Chromosome Heterochromatin in the Anopheles gambiae Complex
Abstract
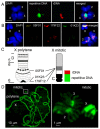
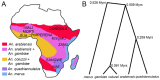
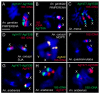
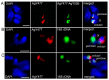
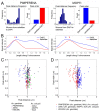
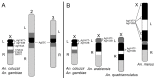
Heterochromatin is identified as a potential factor driving diversification of species. To understand the magnitude of heterochromatin variation within the Anopheles gambiae complex of malaria mosquitoes, we analyzed metaphase chromosomes in An. arabiensis, An. coluzzii, An. gambiae, An. merus, and An. quadriannulatus. Using fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) with ribosomal DNA (rDNA), a highly repetitive fraction of DNA, and heterochromatic Bacterial Artificial Chromosome (BAC) clones, we established the correspondence of pericentric heterochromatin between the metaphase and polytene X chromosomes of An. gambiae. We then developed chromosome idiograms and demonstrated that the X chromosomes exhibit qualitative differences in their pattern of heterochromatic bands and position of satellite DNA (satDNA) repeats among the sibling species with postzygotic isolation, An. arabiensis, An. merus, An. quadriannulatus, and An. coluzzii or An. gambiae. The identified differences in the size and structure of the X chromosome heterochromatin point to a possible role of repetitive DNA in speciation of mosquitoes. We found that An. coluzzii and An. gambiae, incipient species with prezygotic isolation, share variations in the relative positions of the satDNA repeats and the proximal heterochromatin band on the X chromosomes. This previously unknown genetic polymorphism in malaria mosquitoes may be caused by a differential amplification of DNA repeats or an inversion in the sex chromosome heterochromatin.
Keywords: Anopheles; X chromosome; heterochromatin; mitotic chromosome; mosquito; satellite DNA; sex chromosome.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Intraspecific polymorphism of sex chromosome heterochromatin in two species of the Anopheles gambiae complex.Chromosoma. 1980;76(1):57-64. doi: 10.1007/BF00292226. Chromosoma. 1980. PMID: 7358009
-
[Molecular genetic analysis of the X-chromosomal nuclear envelope attachment region in nurse cells of the malaria mosquitoes Anopheles messeae Fall].Genetika. 2011 Oct;47(10):1307-14. Genetika. 2011. PMID: 22232918 Russian.
-
A new chromosomal phylogeny supports the repeated origin of vectorial capacity in malaria mosquitoes of the Anopheles gambiae complex.PLoS Pathog. 2012;8(10):e1002960. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002960. Epub 2012 Oct 4. PLoS Pathog. 2012. PMID: 23055932 Free PMC article.
-
Satellite DNAs and human sex chromosome variation.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Aug;128:15-25. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2022.04.022. Epub 2022 May 27. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35644878 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chromosome speciation: humans, Drosophila, and mosquitoes.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 May 3;102 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):6535-42. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0501847102. Epub 2005 Apr 25. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005. PMID: 15851677 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Plasticity of Genome Architecture.Genes (Basel). 2020 Nov 27;11(12):1413. doi: 10.3390/genes11121413. Genes (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33260806 Free PMC article.
-
Anopheles gambiae Genome Conservation as a Resource for Rational Gene Drive Target Site Selection.Insects. 2021 Jan 23;12(2):97. doi: 10.3390/insects12020097. Insects. 2021. PMID: 33498790 Free PMC article.
-
Transposable element variants and their potential adaptive impact in urban populations of the malaria vector Anopheles coluzzii.Genome Res. 2022 Jan;32(1):189-202. doi: 10.1101/gr.275761.121. Epub 2021 Dec 29. Genome Res. 2022. PMID: 34965939 Free PMC article.
-
Heterochromatin Is Not the Only Place for satDNAs: The High Diversity of satDNAs in the Euchromatin of the Beetle Chrysolina americana (Coleoptera, Chrysomelidae).Genes (Basel). 2024 Mar 22;15(4):395. doi: 10.3390/genes15040395. Genes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38674330 Free PMC article.
-
Chromosome-level genome assemblies of the malaria vectors Anopheles coluzzii and Anopheles arabiensis.Gigascience. 2021 Mar 15;10(3):giab017. doi: 10.1093/gigascience/giab017. Gigascience. 2021. PMID: 33718948 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Davidson G. The Five Mating Types in the Anopheles Gambiae Complex. Riv. Malariol. 1964;43:167–183. - PubMed
-
- Davidson G., Paterson H.E., Coluzzi M., Mason G.F., Micks D.W. The Anopheles gambiae Complex. In: Wright J.W., Pal R., editors. Genetics of Insect Vectors of Diesease. Elsevier Publishing Company; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: London, UK: New York, NY, USA: 1967. pp. 211–249.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

