Effectiveness of orthoses for treatment in patients with spinal pain
- PMID: 32204582
- PMCID: PMC7142031
- DOI: 10.12701/yujm.2020.00150
Effectiveness of orthoses for treatment in patients with spinal pain
Abstract
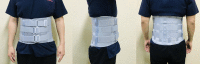
Spinal pain is a common patient complaint in clinical practice. Conservative treatment methods include oral medication, physical therapy, injections, and spinal orthoses. The clinical application of orthoses is debated because of potential complications associated with long-term use, such as muscle weakness and joint contracture. We reviewed the orthoses most frequently used to manage spinal pain. We review the use of soft cervical and Philadelphia collars, lumbosacral corsets, and thoracolumbosacral orthosis to manage spinal pain. Spinal orthoses can help reduce pain by protecting the muscles and joints of the injured spinal region, preventing or correcting malformations, and limiting trunk flexion, extension, lateral flexion, and rotation. The short-term use of spinal orthoses is known to improve pain and disability during the treatment period without significant adverse effects. Spinal orthoses are expected to alleviate pain and improve patients' lifestyle.
Keywords: Conservative treatment; Orthotic devices; Pain; Spine.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures



References
-
- Balague F, Mannion AF, Pellise F, Cedraschi C. Non-specific low back pain. Lancet. 2012;379:482–91. - PubMed
-
- Jang SH, Chang MC. Follow-up of at least five years after lumbar transforaminal epidural steroid injection for radicular pain due to lumbar disc herniation. Ann Palliat Med. 2020;9:116–8. - PubMed
-
- Do KH, Kim TH, Chang MC. Effects of interlaminar epidural steroid injection in patients with moderate to severe lumbar central spinal stenosis. Ann Palliat Med. 2020;9:163–8. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

