Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy following five lines of therapy and three autologous bone marrow transplants for multiple myeloma
- PMID: 32205382
- PMCID: PMC7103853
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2019-233552
Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy following five lines of therapy and three autologous bone marrow transplants for multiple myeloma
Abstract
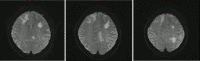
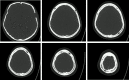
A 59-year-old man, with a background of multiply relapsed myeloma, presented with a 3-week history of confusion, short-term memory impairment and behavioural changes. CT head showed bilateral white matter changes and numerous, large lytic lesions of the skull vault. MRI brain revealed multiple areas of hyperintensity on T2-weighted sequences which did not enhance (many of which showed diffusion restriction) unexpectedly bringing progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML) into the differential. Initial cerebrospinal fluid studies were largely unremarkable, aside from a mildly elevated protein; cultures were negative. PCR for the John Cunningham (JC) virus was positive. Considering the patient's medical history and rapidily progressive symptoms, a palliative approach was adopted, with the patient dying 14 days later. We present this case as an example of PML in a patient with multiple myeloma, highlighting the need to consider this diagnosis in an enlarging population of heavily treated, severely immunocompromised, patients.
Keywords: haematology (drugs and medicines); malignant disease and immunosuppression.
© BMJ Publishing Group Limited 2020. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
