EirA Is a Novel Protein Essential for Intracellular Replication of Coxiella burnetii
- PMID: 32205404
- PMCID: PMC7240097
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.00913-19
EirA Is a Novel Protein Essential for Intracellular Replication of Coxiella burnetii
Abstract
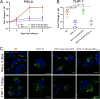
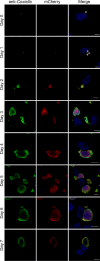
The zoonotic bacterial pathogen Coxiella burnetii is the causative agent of Q fever, a febrile illness which can cause a serious chronic infection. C. burnetii is a unique intracellular bacterium which replicates within host lysosome-derived vacuoles. The ability of C. burnetii to replicate within this normally hostile compartment is dependent on the activity of the Dot/Icm type 4B secretion system. In a previous study, a transposon mutagenesis screen suggested that the disruption of the gene encoding the novel protein CBU2072 rendered C. burnetii incapable of intracellular replication. This protein, subsequently named EirA (
Keywords: Coxiella burnetii; bacterial pathogenesis; host-pathogen interactions; type IV secretion system; virulence factor; virulence factors.
Copyright © 2020 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

