Cow's Milk-Related Symptom Score in Presumed Healthy Polish Infants Aged 0-6 Months
- PMID: 32206628
- PMCID: PMC7073372
- DOI: 10.5223/pghn.2020.23.2.154
Cow's Milk-Related Symptom Score in Presumed Healthy Polish Infants Aged 0-6 Months
Abstract
Purpose: The Cow's Milk-related Symptom Score (CoMiSS™), which considers crying, regurgitation, stools, skin and respiratory symptoms, was developed as an awareness tool for evaluating cow's milk-related symptoms. The scoring ranges from 0 to 33. A score ≥12 was proposed as being likely cow's milk-related and suggestive of allergy to cow's milk. This study aimed to determine the age-related CoMiSS™ values in presumed healthy infants in Poland.
Methods: This was a cross-sectional study conducted in well-child clinics in two locations. Parents of the presumed healthy infants aged ≤6 months were approached during a routine checkup/vaccination visit. The exclusion criteria were as follows: presence of acute or chronic diseases, preterm delivery, treatment with therapeutic formula, and use of any food supplements (except vitamins) or medications.
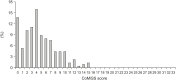
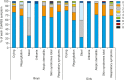
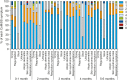
Results: Data from 226 infants were obtained (median age [Q1-Q3], 4 months [3-4]). The overall median (Q1-Q3) and mean (standard deviation) CoMiSS™ values were 4 (2-7) and 4.7 (3.5), respectively. The 95th percentile was 11. Scores on some, albeit not all, components of the CoMiSS™ significantly differed between age groups (crying, stools) or feeding type groups (stools and skin symptoms). Eleven children (4.9%) scored ≥12.
Conclusion: This study adds to earlier age-related CoMiSS™ data by providing CoMiSS™ values in presumed healthy infants in Poland.
Keywords: Food allergy; Food hypersensitivity; Infant; Milk.
Copyright © 2020 by The Korean Society of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: The authors have no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Vandenplas Y, Dupont C, Eigenmann P, Host A, Kuitunen M, Ribes-Koninckx C, et al. A workshop report on the development of the Cow's Milk-related Symptom Score awareness tool for young children. Acta Paediatr. 2015;104:334–339. - PubMed
-
- Zeskind PS. Cross-cultural differences in maternal perceptions of cries of low- and high-risk infants. Child Dev. 1983;54:1119–1128. - PubMed