Intratympanic application of triamcinolone in sudden hearing loss-radiologic anatomy in cone beam CT and its' correlation to clinical outcome
- PMID: 32206871
- PMCID: PMC7286852
- DOI: 10.1007/s00405-020-05920-0
Intratympanic application of triamcinolone in sudden hearing loss-radiologic anatomy in cone beam CT and its' correlation to clinical outcome
Abstract
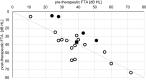
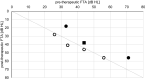
Purpose: To evaluate temporal bone cone-beam CT in patients with idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss (ISSNHL) being treated with primary and secondary intratympanic (IT) triamcinolone and to possibly correlate these results to the clinical outcome.
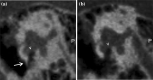
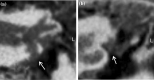
Methods: Retrospective analysis of patients treated with IT triamcinolone for ISSNHL at our department in 2018. Pre- and post-therapeutic audiologic examinations included four-tone average (FTA) at 0.5, 1, 2 and 3 kHz. Using a clinical questionnaire, pre-therapeutic CBCT scans were re-evaluated looking at items, which might interfere with adequate drug diffusion into the inner ear (e.g. bony overhangs or secondary membranes at the round or oval window).
Results: Thirty-one patients were included. Twenty-four (77%; group A) had experienced ineffective systemic steroid therapy before and seven (23%; group B) received primary IT injections. Four group A-patients (21%) and two group B-patients (33%) showed a post-therapeutic FTA improvement of more than 15 dB HL. Bony overhangs at the round window niche (RWN) were present in seven cases (26%), a secondary membrane at the RWN in four (15%) and soft tissue in eight (30%) cases, respectively.
Conclusion: Most patients present radiological findings in CBCT imaging, which might interfere with drug diffusion through the RW membrane. Interestingly, soft or bony tissue obstructing the RWN or the OWN was found in 50% of patients, who showed improvement of hearing. We conclude that radiologic 'tiny' findings are either clinically irrelevant or improvement in hearing is independent from intratympanic drug delivery.
Keywords: Cone-beam CT; Intratympanic injection; Sensorineural hearing loss; Triamcinolone.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Intratympanic Triamcinolone Acetonide as a Salvage Treatment for Idiopathic Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss.Audiol Neurootol. 2021;26(6):425-434. doi: 10.1159/000514086. Epub 2021 Mar 31. Audiol Neurootol. 2021. PMID: 33789267
-
Intratympanic dexamethasone for managing pregnant women with sudden hearing loss.J Int Med Res. 2019 Jan;47(1):377-382. doi: 10.1177/0300060518802725. Epub 2018 Oct 17. J Int Med Res. 2019. PMID: 30328358 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of intermittent intratympanic steroid injection and near-continual transtympanic steroid perfusion as salvage treatments for sudden sensorineural hearing loss.Laryngoscope. 2013 Sep;123(9):2264-9. doi: 10.1002/lary.23909. Epub 2013 Jun 26. Laryngoscope. 2013. PMID: 23804460
-
Intratympanic dexamethasone for sudden sensorineural hearing loss after failure of systemic therapy.Laryngoscope. 2007 Jan;117(1):3-15. doi: 10.1097/01.mlg.0000245058.11866.15. Laryngoscope. 2007. PMID: 17202923 Review.
-
Primary treatment of idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss with intratympanic dexamethasone.Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2016 Oct;24(5):407-12. doi: 10.1097/MOO.0000000000000288. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2016. PMID: 27379547 Review.
Cited by
-
Enhancement in the Round Window Niche: A Potential Pitfall in High-Resolution MR Imaging of the Internal Auditory Canal.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2023 Feb;44(2):176-179. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A7775. Epub 2023 Jan 19. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2023. PMID: 36657949 Free PMC article.
-
Intratympanic Triamcinolone or Dexamethasone in Sudden Sensory Neural Hearing Loss: A Randomized Clinical Trial.Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2023 Dec;75(4):3545-3552. doi: 10.1007/s12070-023-04032-5. Epub 2023 Jul 4. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2023. PMID: 37974838 Free PMC article.
-
Determination of the Round Window Niche Anatomy Using Cone Beam Computed Tomography Imaging as Preparatory Work for Individualized Drug-Releasing Implants.J Imaging. 2021 Apr 26;7(5):79. doi: 10.3390/jimaging7050079. J Imaging. 2021. PMID: 34460675 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Liebau A, Pogorzelski O, Salt AN, Plontke SK. Hearing changes after intratympanically applied steroids for primary therapy of sudden hearing loss: a meta-analysis using mathematical simulations of drug delivery protocols. Otol Neurotol. 2017;38:19–30. doi: 10.1097/MAO.0000000000001254. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

