A Patient with COVID-19 Presenting a False-Negative Reverse Transcriptase Polymerase Chain Reaction Result
- PMID: 32207257
- PMCID: PMC7183837
- DOI: 10.3348/kjr.2020.0195
A Patient with COVID-19 Presenting a False-Negative Reverse Transcriptase Polymerase Chain Reaction Result
Figures
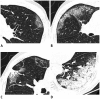
Comment in
-
COVID-19 Carrier or Pneumonia: Positive Real-Time Reverse-Transcriptase Polymerase Chain Reaction but Negative or Positive Chest CT Results.Korean J Radiol. 2020 Jul;21(7):925-928. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2020.0360. Korean J Radiol. 2020. PMID: 32524793 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Comment on
-
False-Negative Results of Real-Time Reverse-Transcriptase Polymerase Chain Reaction for Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2: Role of Deep-Learning-Based CT Diagnosis and Insights from Two Cases.Korean J Radiol. 2020 Apr;21(4):505-508. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2020.0146. Epub 2020 Mar 5. Korean J Radiol. 2020. PMID: 32174053 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Li D, Wang D, Dong J, Wang N, Huang H, Xu H, et al. False-negative results of real-time reverse-transcriptase polymerase chain reaction for severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2: role of deep-learning-based CT diagnosis and insights from two cases. Korean J Radiol. 2020;21:505–508. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

