Fluorescent Probes for Monitoring Serine Ubiquitination
- PMID: 32207972
- PMCID: PMC7294441
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.biochem.0c00067
Fluorescent Probes for Monitoring Serine Ubiquitination
Abstract
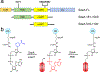
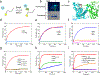
In a radical departure from the classical E1-E2-E3 three-enzyme mediated ubiquitination of eukaryotes, the recently described bacterial enzymes of the SidE family of Legionella pneumophila effectors utilize NAD+ to ligate ubiquitin onto target substrate proteins. This outcome is achieved via a two-step mechanism involving (1) ADP ribosylation of ubiquitin followed by (2) phosphotransfer to a target serine residue. Here, using fluorescent NAD+ analogues as well as synthetic substrate mimics, we have developed continuous assays enabling real-time monitoring of both steps of this mechanism. These assays are amenable to biochemical studies and high-throughput screening of inhibitors of these effectors, and the discovery and characterization of putative enzymes similar to members of the SidE family in other organisms. We also show their utility in studying enzymes that can reverse and inhibit this post-translational modification.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
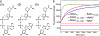
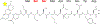
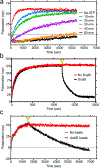
References
-
- Komander D, and Rape M (2012) The Ubiquitin Code. Annu. Rev. Biochem 81 (1), 203–229. - PubMed
-
- Ashida H, Kim M, and Sasakawa C (2014) Exploitation of the Host Ubiquitin System by Human Bacterial Pathogens. Nat. Rev. Microbiol 12 (6), 399–413. - PubMed
-
- Qiu J, and Luo Z-Q (2017) Legionella and Coxiella Effectors: Strength in Diversity and Activity. Nat. Rev. Microbiol 15 (10), 591–605. - PubMed
-
- Bhogaraju S, Kalayil S, Liu Y, Bonn F, Colby T, Matic I, and Dikic I (2016) Phosphoribosylation of Ubiquitin Promotes Serine Ubiquitination and Impairs Conventional Ubiquitination. Cell 167 (6), 1636–1649.e13. - PubMed

