Consecutive Charging of a Perylene Bisimide Dye by Multistep Low-Energy Solar-Light-Induced Electron Transfer Towards H2 Evolution
- PMID: 32208545
- PMCID: PMC7317913
- DOI: 10.1002/anie.202001231
Consecutive Charging of a Perylene Bisimide Dye by Multistep Low-Energy Solar-Light-Induced Electron Transfer Towards H2 Evolution
Abstract
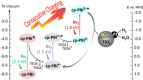
A photocatalytic system containing a perylene bisimide (PBI) dye as a photosensitizer anchored to titanium dioxide (TiO2 ) nanoparticles through carboxyl groups was constructed. Under solar-light irradiation in the presence of sacrificial triethanolamine (TEOA) in neutral and basic conditions (pH 8.5), a reaction cascade is initiated in which the PBI molecule first absorbs green light, giving the formation of a stable radical anion (PBI.- ), which in a second step absorbs near-infrared light, forming a stable PBI dianion (PBI2- ). Finally, the dianion absorbs red light and injects an electron into the TiO2 nanoparticle that is coated with platinum co-catalyst for hydrogen evolution. The hydrogen evolution rates (HERs) are as high as 1216 and 1022 μmol h-1 g-1 with simulated sunlight irradiation in neutral and basic conditions, respectively.
Keywords: electron transfer; hydrogen evolution; nanoparticles; perylene bisimides; solar energy.
© 2020 The Authors. Published by Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Kudo A., Miseki Y., Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 253–278. - PubMed
-
- Berardi S., Drouet S., Francas L., Gimbert-Surinach C., Guttentag M., Richmond C., Stoll T., Llobet A., Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 7501–7519. - PubMed
-
- Li X.-B., Gao Y.-J., Wang Y., Zhan F., Zhang X.-Y., Kong Q.-Y., Zhao N.-J., Guo Q., Wu H.-L., Li Z.-J., Tao Y., Zhang J.-P., Chen B., Tung C.-H., Wu L.-Z., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 4789–4796. - PubMed
-
- Choi S. K., Yang H. S., Kim J. H., Park H., Appl. Catal. B 2012, 121–122, 206–213.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

