Cognitive and clinical predictors of community functioning across the psychoses
- PMID: 32208557
- PMCID: PMC7179050
- DOI: 10.1002/pchj.356
Cognitive and clinical predictors of community functioning across the psychoses
Abstract
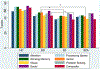
Schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and related psychotic illnesses are common, serious mental disorders that are often associated with functional impairments and poor quality of life, even after clinical recovery. Cognitive dysfunction is a strong predictor of functional impairment; however, findings regarding relative impairments in functioning and cognition across diagnoses have been mixed, as have reports of the contribution of clinical symptoms and other illness features to functioning across diagnostic boundaries. We assessed 211 patients with psychotic disorders and 87 healthy controls using the MATRICS Consensus Cognitive Battery, clinical measures of state mood and psychotic symptoms, and an interview measure of community functioning. Diagnostic groups were compared on MATRICS composite and domain scores, and clinical and functional measures. We then examined cognitive, clinical, and demographic predictors of community functioning using stepwise hierarchical linear regression. All three patient groups exhibited deficits in most cognitive domains relative to controls, and significantly poorer community functioning. While scores on most cognitive domains did not differ by diagnosis, when groups did differ patients with schizophrenia performed worse than patients with bipolar disorder. Cognition was correlated with functioning across the sample. The final regression model included negative symptoms, mania, social cognition, and processing speed, and explained 47% of the variance in community functioning scores across patient groups. Residual negative symptoms, residual mania, and social cognition significantly and independently predicted community functioning. These findings indicate that, while all cognitive domains are associated with community outcomes, when considered together and with clinical symptoms, negative symptoms, mania, and social cognition are the strongest predictors across diagnoses. Development of interventions targeting negative symptoms and social cognition may be effective in improving community functioning for patients across diagnoses.
Keywords: bipolar; cognition; functioning; schizoaffective; schizophrenia; social cognition.
© 2020 The Institute of Psychology, Chinese Academy of Sciences and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose in association with this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Clinical and cognitive factors affecting psychosocial functioning in remitted patients with bipolar disorder.Psychiatriki. 2016 Jul-Sep;27(3):182-191. doi: 10.22365/jpsych.2016.273.182. Psychiatriki. 2016. PMID: 27837572
-
Neuropsychological functioning predicts community outcomes in affective and non-affective psychoses: a 6-month follow-up.Schizophr Res. 2013 Aug;148(1-3):34-7. doi: 10.1016/j.schres.2013.05.012. Epub 2013 Jun 19. Schizophr Res. 2013. PMID: 23791391 Free PMC article.
-
Examining cognition across the bipolar/schizophrenia diagnostic spectrum.J Psychiatry Neurosci. 2018 Jul;43(4):245-253. doi: 10.1503/jpn.170076. J Psychiatry Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29947606 Free PMC article.
-
[How to differentiate schizophrenia from bipolar disorder using cognitive assessment?].Encephale. 2009 Apr;35(2):139-45. doi: 10.1016/j.encep.2008.03.011. Epub 2008 Sep 23. Encephale. 2009. PMID: 19393382 Review. French.
-
Cognitive and psychomotor effects of risperidone in schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder.Clin Ther. 2008 Sep;30(9):1565-89. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2008.09.014. Clin Ther. 2008. PMID: 18840365 Review.
Cited by
-
Affective lability and social functioning in severe mental disorders.Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2022 Aug;272(5):873-885. doi: 10.1007/s00406-022-01380-1. Epub 2022 Jan 27. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35084540 Free PMC article.
-
Relationships between cognition and symptoms across mood and psychotic disorders.Psychiatry Res. 2025 Sep;351:116628. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2025.116628. Epub 2025 Jul 8. Psychiatry Res. 2025. PMID: 40680693 Free PMC article.
-
European Psychiatric Association guidance on assessment of cognitive impairment in schizophrenia.Eur Psychiatry. 2022 Sep 5;65(1):e58. doi: 10.1192/j.eurpsy.2022.2316. Eur Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 36059109 Free PMC article.
-
The relations between executive functions and occupational functioning in individuals with bipolar disorder: a scoping review.Int J Bipolar Disord. 2022 Mar 14;10(1):8. doi: 10.1186/s40345-022-00255-7. Int J Bipolar Disord. 2022. PMID: 35286505 Free PMC article.
-
Real-World Functioning in Psychiatric Outpatients: Predictive Factors.J Clin Med. 2022 Jul 28;11(15):4400. doi: 10.3390/jcm11154400. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 35956015 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

