Epigenetic modulations of noncoding RNA: a novel dimension of Cancer biology
- PMID: 32209098
- PMCID: PMC7092482
- DOI: 10.1186/s12943-020-01159-9
Epigenetic modulations of noncoding RNA: a novel dimension of Cancer biology
Abstract
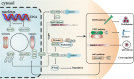
Empowered by recent advances of sequencing techniques, transcriptome-wide studies have characterized over 150 different types of post-transcriptional chemical modifications of RNA, ranging from methylations of single base to complex installing reactions catalyzed by coordinated actions of multiple modification enzymes. These modifications have been shown to regulate the function and fate of RNAs and further affecting various cellular events. However, the current understanding of their biological functions in human diseases, especially in cancers, is still limited. Once regarded as "junk" or "noise" of the transcriptome, noncoding RNA (ncRNA) has been proved to be involved in a plethora of cellular signaling pathways especially those regulating cancer initiation and progression. Accumulating evidence has demonstrated that ncRNAs manipulate multiple phenotypes of cancer cells including proliferation, metastasis and chemoresistance and may become promising biomarkers and targets for diagnosis and treatment of cancer. Importantly, recent studies have mapped plenty of modified residues in ncRNA transcripts, indicating the existence of epigenetic modulation of ncRNAs and the potential effects of RNA modulation on cancer progression. In this review, we briefly introduced the characteristics of several main epigenetic marks on ncRNAs and summarized their consecutive effects on cancer cells. We found that ncRNAs could act both as regulators and targets of epigenetic enzymes, which indicated a cross-regulating network in cancer cells and unveil a novel dimension of cancer biology. Moreover, by epitomizing the knowledge of RNA epigenetics, our work may pave the way for the design of patient-tailored therapeutics of cancers.
Keywords: Cancer progression; Cancer treatment; Noncoding RNA; RNA epigenetics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

