ACE inhibitors in SSc patients display a risk factor for scleroderma renal crisis-a EUSTAR analysis
- PMID: 32209135
- PMCID: PMC7093969
- DOI: 10.1186/s13075-020-2141-2
ACE inhibitors in SSc patients display a risk factor for scleroderma renal crisis-a EUSTAR analysis
Abstract
Objectives: To investigate the effect of ACE inhibitors (ACEi) on the incidence of scleroderma renal crisis (SRC) when given prior to SRC in the prospectively collected cohort from the European Scleroderma Trial and Research Group (EUSTAR).
Methods: SSc patients without prior SRC and at least one follow-up visit were included and analyzed regarding SRC, arterial hypertension, and medication focusing on antihypertensive medication and glucocorticoids (GC).
Results: Out of 14,524 patients in the database, we identified 7648 patients with at least one follow-up. In 27,450 person-years (py), 102 patients developed SRC representing an incidence of 3.72 (3.06-4.51) per 1000 py. In a multivariable time-to-event analysis adjusted for age, sex, disease severity, and onset, 88 of 6521 patients developed SRC. The use of ACEi displayed an increased risk for the development of SRC with a hazard ratio (HR) of 2.55 (95% confidence interval (CI) 1.65-3.95). Adjusting for arterial hypertension resulted in a HR of 2.04 (95%CI 1.29-3.24). There was no evidence for an interaction of ACEi and arterial hypertension (HR 0.83, 95%CI 0.32-2.13, p = 0.69). Calcium channel blockers (CCB), angiotensin receptor blockers (ARB), endothelin receptor antagonists, and GC-mostly in daily dosages below 15 mg of prednisolone-did not influence the hazard for SRC.
Conclusions: ACEi in SSc patients with concomitant arterial hypertension display an independent risk factor for the development of SRC but are still first choice in SRC treatment. ARBs might be a safe alternative, yet the overall safety of alternative antihypertensive drugs in SSc patients needs to be further studied.
Keywords: ACE inhibitors; Antihypertensive drugs; Arterial hypertension; Outcome; Scleroderma renal crisis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


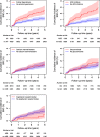
References
-
- Hudson M, Baron M, Tatibouet S, Furst DE, Khanna D. International scleroderma renal crisis study I. Exposure to ACE inhibitors prior to the onset of scleroderma renal crisis-results from the international scleroderma renal crisis survey. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2014;43(5):666–672. doi: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2013.09.008. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

