Computers and viral diseases. Preliminary bioinformatics studies on the design of a synthetic vaccine and a preventative peptidomimetic antagonist against the SARS-CoV-2 (2019-nCoV, COVID-19) coronavirus
- PMID: 32209231
- PMCID: PMC7094376
- DOI: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2020.103670
Computers and viral diseases. Preliminary bioinformatics studies on the design of a synthetic vaccine and a preventative peptidomimetic antagonist against the SARS-CoV-2 (2019-nCoV, COVID-19) coronavirus
Abstract
This paper concerns study of the genome of the Wuhan Seafood Market isolate believed to represent the causative agent of the disease COVID-19. This is to find a short section or sections of viral protein sequence suitable for preliminary design proposal for a peptide synthetic vaccine and a peptidomimetic therapeutic, and to explore some design possibilities. The project was originally directed towards a use case for the Q-UEL language and its implementation in a knowledge management and automated inference system for medicine called the BioIngine, but focus here remains mostly on the virus itself. However, using Q-UEL systems to access relevant and emerging literature, and to interact with standard publically available bioinformatics tools on the Internet, did help quickly identify sequences of amino acids that are well conserved across many coronaviruses including 2019-nCoV. KRSFIEDLLFNKV was found to be particularly well conserved in this study and corresponds to the region around one of the known cleavage sites of the SARS virus that are believed to be required for virus activation for cell entry. This sequence motif and surrounding variations formed the basis for proposing a specific synthetic vaccine epitope and peptidomimetic agent. The work can, nonetheless, be described in traditional bioinformatics terms, and readily reproduced by others, albeit with the caveat that new data and research into 2019-nCoV is emerging and evolving at an explosive pace. Preliminary studies using molecular modeling and docking, and in that context the potential value of certain known herbal extracts, are also described.
Keywords: 2019-nCoV coronavirus; Automatic browser; Bioinformatics; Peptidomimetic; Q-UEL language; Retroinverso; Synthetic vaccine; Wuhan seafood market coronavirus.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest This paper is provided to the community to promote the more general applications of the thinking of Professor Paul A. M. Dirac in human and animal medicine in accordance with the charter of The Dirac Foundation, to emphasize the advantages and simplicity of the basic form of the Hyperbolic Dirac Net, to encourage its use, and to propose at least some of the principles of the associated Q-UEL, a universal exchange language for medicine, as a basis for a standard for interoperability. These mathematical and engineering principles are used, amongst many others in an integrated way, in the algorithms and internal architectural features of the BioIngine.com, a distributed system developed by Ingine Inc. Cleveland, Ohio, for the mining of, and inference from, Very Big Data for commercial purposes.
Figures
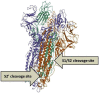
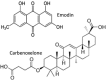








References
-
- Robson B. 2010. Preliminary Bioinformatics Studies on the Design of Synthetic Vaccines and Preventative Peptidomimetic Antagonists against the Wuhan Seafood Market Coronavirus. Possible Importance of the KRSFIEDLLFNKV Motif, Circulated and Published on ResearchGate. - DOI
-
- Wu F., Zhao S., Yu B., Chen Y.-M., Wang W., Hu Y., Song Z.-G., Tao Z.-W., Tian J.-H., Pei Y.-Y., Yuan M.L., Zhang Y.-L., Dai F.-H., Liu Y., Wang Q.-M., Zheng J.-J., Xu L., Holmes E.C., Zhang Y.-Z. 2019. A Novel Coronavirus Associated with a Respiratory Disease in Wuhan of Hubei Province, China, , Wuhan Seafood Market Pneumonia Virus Isolate Wuhan-Hu-1, Complete Genome.https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/nuccore/MN908947 GenBank submission MN908947.3.
-
- Kam Y.W., Okumura Y., Kido H., Ng L.F.P., Bruzzone R., Altmeyer R. Cleavage of the SARS coronavirus spike glycoprotein by airway proteases enhances virus entry into human bronchial epithelial cells in vitro published. PloS One. 2009 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0007870. November 17. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Recent Papers
-
- Robson B. Quantum universal exchange language and hyperbolic Dirac nets for precision medicine and drug design. Proposals with examples from mitochondrial studies. Comput. Biol. Med. February, 2016;117 - PubMed
-
- Robson B. Bidirectional General Graphs for inference. Principles and implications for medicine. Comput. Biol. Med. 2019;10:382–399. (2019) - PubMed
-
- Robson B., Boray S. Studies in the extensively automatic construction of large odds-based inference networks from structured data. Examples from medical, bioinformatics, and health insurance claims data. Comput. Biol. Med. 2018;95:147–166. - PubMed
-
- Robson B. Studies in using a universal exchange and inference language for evidence based medicine. Semi-automated learning and reasoning for PICO methodology, systematic review, and environmental epidemiology. Comput. Biol. Med. 2016;79:299–323. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

