Wuhan and Hubei COVID-19 mortality analysis reveals the critical role of timely supply of medical resources
- PMID: 32209384
- PMCID: PMC7163181
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jinf.2020.03.018
Wuhan and Hubei COVID-19 mortality analysis reveals the critical role of timely supply of medical resources
Abstract
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
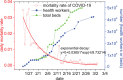
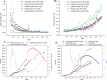
Comment in
-
Flattening-the-curve associated with reduced COVID-19 case fatality rates- an ecological analysis of 65 countries.J Infect. 2020 Jul;81(1):e98-e99. doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2020.04.007. Epub 2020 Apr 17. J Infect. 2020. PMID: 32305488 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Risk factors associated with disease severity and length of hospital stay in COVID-19 patients.J Infect. 2020 Jul;81(1):e95-e97. doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2020.04.008. Epub 2020 Apr 17. J Infect. 2020. PMID: 32305490 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- WHO: Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) outbreak. Available from: https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019. visited on 4 March, 2020.
-
- The National Health Commission of China, real-time data of the COVID-19 outbreaks in China (in Chinese), http://www.nhc.gov.cn/xcs/yqfkdt/gzbd_index.shtml. accessed on 4 March, 2020.
-
- The Novel Coronavirus Pneumonia Emergency Response Epidemiology Team. Vital surveillances: the epidemiological characteristics of an outbreak of 2019 novel coronavirus diseases (COVID-19)—China, 2020, http://weekly.chinacdc.cn/en/article/id/e53946e2-c6c4-41e9-9a9b-fea8db1a..., in China CDC Weekly. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

