Management strategy of novel coronavirus (COVID-19) pneumonia in the radiology department: a Chinese experience
- PMID: 32209526
- PMCID: PMC7239366
- DOI: 10.5152/dir.2020.20167
Management strategy of novel coronavirus (COVID-19) pneumonia in the radiology department: a Chinese experience
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
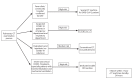
Figures


References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

