Insights into platinum-induced peripheral neuropathy-current perspective
- PMID: 32209761
- PMCID: PMC7437596
- DOI: 10.4103/1673-5374.276321
Insights into platinum-induced peripheral neuropathy-current perspective
Abstract
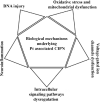
Cancer is a global health problem that is often successfully addressed by therapy, with cancer survivors increasing in numbers and living longer world around. Although new cancer treatment options are continuously explored, platinum based chemotherapy agents remain in use due to their efficiency and availability. Unfortunately, all cancer therapies affect normal tissues as well as cancer, and more than 40 specific side effects of platinum based drugs documented so far decrease the quality of life of cancer survivors. Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy is a frequent side effects of platinum-based chemotherapy agents. This cluster of complications is often so debilitating that patients occasionally have to discontinue the therapy. Sensory neurons of dorsal root ganglia are at the core of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy symptoms. In these postmitotic cells, DNA damage caused by platinum chemotherapy interferes with normal functioning. Accumulation of DNA-platinum adducts correlates with neurotoxic severity and development of sensation of pain. While biochemistry of DNA-platinum adducts is the same in all cell types, molecular mechanisms affected by DNA-platinum adducts are different in cancer cells and non-dividing cells. This review aims to raise awareness about platinum associated chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy as a medical problem that has remained unexplained for decades. We emphasize the complexity of this condition both from clinical and mechanistical point of view and focus on recent findings about chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy in in vitro and in vivo model systems. Finally, we summarize current perspectives about clinical approaches for chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy treatment.
Keywords: CIPN; DNA-Pt adducts; DRG; Pt; chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy; dorsal root ganglia; model systems; molecular mechanisms; neurotoxic; platinum based chemotherapy; sensory neurons treatment; side effects.
Conflict of interest statement
None
Figures
Similar articles
-
Meclizine and Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor Agonists Attenuate Severe Pain and Ca2+ Activity of Primary Sensory Neurons in Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy.J Neurosci. 2022 Aug 3;42(31):6020-6037. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1064-21.2022. J Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35772967 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Nucleotide Excision Repair in Cisplatin-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy: Mechanism, Prevention, and Treatment.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Feb 17;22(4):1975. doi: 10.3390/ijms22041975. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33671279 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Association of Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy Symptoms and the Risk of Falling.JAMA Neurol. 2016 Jul 1;73(7):860-6. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2016.0383. JAMA Neurol. 2016. PMID: 27183099 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting dorsal root ganglia for chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: from bench to bedside.Ther Adv Neurol Disord. 2024 Sep 20;17:17562864241252718. doi: 10.1177/17562864241252718. eCollection 2024. Ther Adv Neurol Disord. 2024. PMID: 39318973 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long-Term Effects, Pathophysiological Mechanisms, and Risk Factors of Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathies: A Comprehensive Literature Review.Front Pharmacol. 2017 Feb 24;8:86. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2017.00086. eCollection 2017. Front Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28286483 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Synergistic effects of olaparib combined with ERCC1 on the sensitivity of cisplatin in non-small cell lung cancer.Oncol Lett. 2021 May;21(5):365. doi: 10.3892/ol.2021.12626. Epub 2021 Mar 10. Oncol Lett. 2021. PMID: 33747222 Free PMC article.
-
Peripheral neuropathy associated with monomethyl auristatin E-based antibody-drug conjugates.iScience. 2023 Aug 29;26(10):107778. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.107778. eCollection 2023 Oct 20. iScience. 2023. PMID: 37727735 Free PMC article. Review.
-
KLS-13019, a Novel Structural Analogue of Cannabidiol and GPR55 Receptor Antagonist, Prevents and Reverses Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy in Rats.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2024 Oct 18;391(2):231-240. doi: 10.1124/jpet.124.002190. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2024. PMID: 39134424
-
Pharmacotherapy of Neuropathic Pain.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 Jun 19;18(6):930. doi: 10.3390/ph18060930. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40573324 Free PMC article.
-
Considerations for a Reliable In Vitro Model of Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy.Toxics. 2021 Nov 11;9(11):300. doi: 10.3390/toxics9110300. Toxics. 2021. PMID: 34822690 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Albers J, Chaudhry V, Cavaletti G, Donehower R. Interventions for preventing neuropathy caused by cisplatin and related compounds. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007;1:Cd005228. - PubMed
-
- Ali I, Wani WA, Saleem K, Haque A. Platinum compounds: a hope for future cancer chemotherapy. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2013;13:296–306. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

