Epidemiological data from the COVID-19 outbreak, real-time case information
- PMID: 32210236
- PMCID: PMC7093412
- DOI: 10.1038/s41597-020-0448-0
Epidemiological data from the COVID-19 outbreak, real-time case information
Abstract
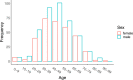
Cases of a novel coronavirus were first reported in Wuhan, Hubei province, China, in December 2019 and have since spread across the world. Epidemiological studies have indicated human-to-human transmission in China and elsewhere. To aid the analysis and tracking of the COVID-19 epidemic we collected and curated individual-level data from national, provincial, and municipal health reports, as well as additional information from online reports. All data are geo-coded and, where available, include symptoms, key dates (date of onset, admission, and confirmation), and travel history. The generation of detailed, real-time, and robust data for emerging disease outbreaks is important and can help to generate robust evidence that will support and inform public health decision making.
Conflict of interest statement
SM declares employment at Booz Allen Hamilton while engaged in the research project. All other authors declare no competing financial interests.