Immune response against Chlamydia trachomatis via toll-like receptors is negatively regulated by SIGIRR
- PMID: 32210474
- PMCID: PMC7094862
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0230718
Immune response against Chlamydia trachomatis via toll-like receptors is negatively regulated by SIGIRR
Abstract
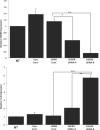
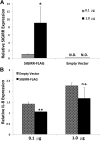
Chlamydia trachomatis is the most common bacterial sexually-transmitted infection and the major cause of preventable blindness worldwide. The asymptomatic nature of many infections along with uncontrolled inflammation leads to irreversible damage in the upper genital tract and the tarsal conjunctivae, with the major complications of infertility and chronic pelvic pain, and blindness, respectively. Inflammation must, therefore, be tightly regulated to avoid an unrestrained immune response. The genetic factors that regulate inflammation through Toll-like receptor (TLR) signaling pathways during C. trachomatis infection have not been fully characterized. SIGIRR (also known as IL-1R8 or TIR8) can regulate inflammation in response to various pathogens and diseases. However, nothing is known about its role during C. trachomatis infection. Expression of the pro-inflammatory chemokine, IL-8, was measured in epithelial cells infected with C. trachomatis. The effect of SIGIRR was determined by depleting SIGIRR or over-expressing SIGIRR in the epithelial cells before infection. Our results indicate that, in the absence of SIGIRR, epithelial cells induce higher levels of the pro-inflammatory chemokine, IL-8, in response to C. trachomatis infection. In addition, SIGIRR associates with MyD88 in both infected and uninfected infected cells. Collectively, our data demonstrate that SIGIRR functions as a negative regulator of the immune response to C. trachomatis infection. This finding provides insights into the immuno-pathogenesis of C. trachomatis that can be used to treat and identify individuals at risk of uncontrolled inflammation during infection.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures