Distinctive Gene Expression Profiles and Effectors Consistent With Host Specificity in Two Formae Speciales of Marssonina brunnea
- PMID: 32210930
- PMCID: PMC7076119
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.00276
Distinctive Gene Expression Profiles and Effectors Consistent With Host Specificity in Two Formae Speciales of Marssonina brunnea
Abstract
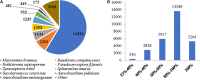
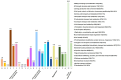
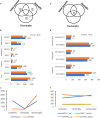
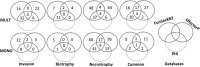
The knowledge on the host specificity of a pathogen underlying an interaction is becoming an urgent necessity for global warming. In this study, the gene expression profiles and the roles of effectors in host specificity were integrally characterized with two formae speciales, multigermtubi and monogermtubi, of a hemibiotrophic pathogen Marssonina brunnea when they were infecting respective susceptible poplar hosts. With a functional genome comparison referring to a de novo transcriptome of M. brunnea and Pathogen-Host Interaction database functional annotations, the multigermtubi strain showed abundant and significant differentially expressed unigenes (DEGs) (more than 40%) in colonizing the initial invasion stage and in the necrotrophic stage. The monogermtubi strain induced less than 10% of DEGs in the initial invasion stage but which abruptly increased to more than 80% DEGs in the necrotrophic stage. Both strains induced the least DEGs in the biotrophic stage compared to the initial invasion and necrotrophic stages. The orthologs of the effector genes Ecp6, PemG1, XEG1, ACE1, and Mg3LysM were exclusively induced by one of the two formae speciales depending on the infection stages. Some unigenes homologous to carbohydrate lytic enzyme genes, especially pectate lyases, were notably induced with multigermtubi forma specialis infection but not expressed in the monogermtubi forma specialis at an earlier infection stage. The extraordinary differences in the functional genome level between the two formae speciales of M. brunnea could be fundamental to exploring their host specificity determinant and evolution. This study also firstly provided the fungal transcriptome of the monogermtubi forma specialis for M. brunnea.
Keywords: Marssonina brunnea; de novo transcriptome; disease; effectors; forma specialis; host specificity; poplar.
Copyright © 2020 Ren, Yan, Wu, Sun, Song and Li.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Genome-Wide Transcriptome Analysis Reveals the Comprehensive Response of Two Susceptible Poplar Sections to Marssonina brunnea Infection.Genes (Basel). 2018 Mar 12;9(3):154. doi: 10.3390/genes9030154. Genes (Basel). 2018. PMID: 29534547 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome Analysis and Reactive Oxygen Species Detection Suggest Contrasting Molecular Mechanisms in Populus canadensis' Response to Different Formae Speciales of Marssonina brunnea.Genes (Basel). 2024 Jan 18;15(1):116. doi: 10.3390/genes15010116. Genes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38255004 Free PMC article.
-
Use of Comparative Genomics-Based Markers for Discrimination of Host Specificity in Fusarium oxysporum.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2017 Dec 15;84(1):e01868-17. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01868-17. Print 2018 Jan 1. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 29030446 Free PMC article.
-
Current Status of Fusarium oxysporum Formae Speciales and Races.Phytopathology. 2019 Apr;109(4):512-530. doi: 10.1094/PHYTO-08-18-0320-RVW. Epub 2019 Mar 4. Phytopathology. 2019. PMID: 30461350 Review.
-
Sequencing the genome of Marssonina brunnea reveals fungus-poplar co-evolution.BMC Genomics. 2012 Aug 9;13:382. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-13-382. BMC Genomics. 2012. PMID: 22876864 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Editing Metabolism, Sex, and Microbiome: How Can We Help Poplar Resist Pathogens?Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 21;25(2):1308. doi: 10.3390/ijms25021308. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38279306 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic variation along an altitudinal gradient in the Phytophthora infestans effector gene Pi02860.Front Microbiol. 2022 Sep 8;13:972928. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.972928. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36160230 Free PMC article.
-
The responses of poplars to fungal pathogens: A review of the defensive pathway.Front Plant Sci. 2023 Feb 16;14:1107583. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1107583. eCollection 2023. Front Plant Sci. 2023. PMID: 36875570 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rapid and Specific Detection of the Poplar Black Spot Disease Caused by Marssonina brunnea Using Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Assay.Plants (Basel). 2021 Jan 28;10(2):253. doi: 10.3390/plants10020253. Plants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33525490 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

