A Uniquely Altered Oral Microbiome Composition Was Observed in Pregnant Rats With Porphyromonas gingivalis Induced Periodontal Disease
- PMID: 32211345
- PMCID: PMC7069352
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.00092
A Uniquely Altered Oral Microbiome Composition Was Observed in Pregnant Rats With Porphyromonas gingivalis Induced Periodontal Disease
Abstract
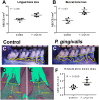
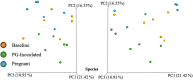
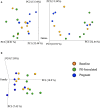
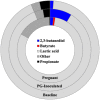
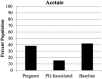
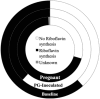
Porphyromonas gingivalis is an anaerobic bacterium commonly found in the oral cavity and associated with the development of periodontal disease. P. gingivalis has also been linked to several systemic vascular and inflammatory diseases including poor pregnancy outcomes. Little is known about the changes in the oral flora during pregnancy in connection to P. gingivalis infection. This pilot study aims to explore changes in the oral microbiome due to P. gingivalis inoculation and pregnancy in an in vivo rat model of periodontal disease. A metagenomic sequencing analysis targeting seven of the 16S rRNA gene variable regions was performed for oral samples collected at the following time points: baseline control (week 0), P. gingivalis inoculated (week 11), P. gingivalis inoculated and pregnant rat at necropsy (week 16). A second set of animals were also sampled to generate a sham-inoculated (week 11) control group. We found that the rat oral microbiome profiles were more similar to that of the human oral cavity compared to previous reports targeting one or two 16S variable regions. Overall, there appears to be a relatively stable core microbiome in the oral cavity. As expected, P. gingivalis induced periodontal disease resulted in oral microbiome dysbiosis. During pregnancy, some aspects of the oral microbiome shifted toward a more baseline-like profile. However, population analyses in terms of dissimilarity measures and especially metagenomic based predictions of select characteristics such as cell morphology, oxygen requirement, and major metabolite synthesis showed that pregnancy did not restore the composition of the oral microbiome. Rather, a uniquely altered oral microbiome composition was observed in pregnant rats with pre-established periodontal disease.
Keywords: microbial metabolites; oral microbiome; oxygen requirement; periodontal disease; pregnancy; rat model.
Copyright © 2020 Walkenhorst, Reyes, Perez, Progulske-Fox, Brown and Phillips.
Figures







References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

