Risk factors for non-closure of an intended temporary defunctioning stoma after emergency resection of left-sided obstructive colon cancer
- PMID: 32211956
- PMCID: PMC7245586
- DOI: 10.1007/s00384-020-03559-1
Risk factors for non-closure of an intended temporary defunctioning stoma after emergency resection of left-sided obstructive colon cancer
Abstract
Purpose: A substantial part (21-35%) of defunctioning stomas created during resection for colorectal cancer will never be reversed. Known risk factors for non-closure are age, peri- or postoperative complications, comorbidity, and tumor stage. However, studies performed to identify these risk factors mostly focus on rectal cancer and include both preoperative and postoperative factors. This study aims to identify preoperative risk factors for non-reversal of intended temporary stomas created during acute resection of left-sided obstructive colon cancer (LSOCC) with primary anastomosis.
Methods: All patients who underwent emergency resection for LSOCC with primary anastomosis and a defunctioning stoma between 2009 and 2016 were selected from the Dutch ColoRectal Audit, and additional data were collected in the local centers. Multivariable analysis was performed to identify independent preoperative factors for non-closure of the stoma.
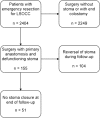
Results: A total of 155 patients underwent acute resection for LSOCC with primary anastomosis and a defunctioning stoma. Of these, 51 patients (32.9%) did not have their stoma reversed after a median of 53 (range 7-104) months of follow-up. In multivariable analysis, hemoglobin < 7.5 mmol/L (odds ratio (OR) 4.79, 95% confidence interval (95% CI) 1.60-14.38, p = 0.005), estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) ≤ 45 mL/min/1.73 m2 (OR 4.64, 95% CI 1.41-15.10, p = 0.011), and metastatic disease (OR 6.12, 95% CI 2.35-15.94, p < 0.001) revealed to be independent predictors of non-closure.
Conclusions: Anemia, impaired renal function, and metastatic disease at presentation were found to be independent predictors for non-reversal of intended temporary stomas in patients who underwent acute resection for LSOCC. In patients who have an increased risk of non-reversal, the surgeon should consider a Hartmann's procedure.
Keywords: Colorectal cancer; Defunctioning stoma; Non-closure; Obstructive colon cancer; Stoma reversal; Surgical oncology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
References
-
- Öistämö E, Hjern F, Blomqvist L, Falkén Y, Pekkari K, Abraham-Nordling M. Emergency management with resection versus proximal stoma or stent treatment and planned resection in malignant left-sided colon obstruction. World J Surg Oncol. 2016;14:232. doi: 10.1186/s12957-016-0994-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Arezzo A, Passera R, Lo Secco G, Verra M, Bonino MA, Targarona E, Morino M. Stent as bridge to surgery for left-sided malignant colonic obstruction reduces adverse events and stoma rate compared with emergency surgery: results of a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Gastrointest Endosc. 2017;86(3):416–426. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2017.03.1542. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Den Dulk M, Smit M, Peeters KC, Kranenbarg EM, Rutten HJ, Wiggers T, et al. A multivariate analysis of limiting factors for stoma reversal in patients with rectal cancer entered into the total mesorectal excision (TME) trial: a retrospective study. Lancet Oncol. 2007;8:297–303. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(07)70047-5. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous