Clinical Potential of Targeting Fibroblast Growth Factor-23 and αKlotho in the Treatment of Uremic Cardiomyopathy
- PMID: 32212912
- PMCID: PMC7428638
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.120.016041
Clinical Potential of Targeting Fibroblast Growth Factor-23 and αKlotho in the Treatment of Uremic Cardiomyopathy
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Clinical Potential of Targeting Fibroblast Growth Factor-23 and αKlotho in the Treatment of Uremic Cardiomyopathy.J Am Heart Assoc. 2020 Jul 21;9(14):e014566. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.119.014566. Epub 2020 Jul 17. J Am Heart Assoc. 2020. PMID: 32674722 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Chronic kidney disease is highly prevalent, affecting 10% to 15% of the adult population worldwide and is associated with increased cardiovascular morbidity and mortality. As chronic kidney disease worsens, a unique cardiovascular phenotype develops characterized by heart muscle disease, increased arterial stiffness, atherosclerosis, and hypertension. Cardiovascular risk is multifaceted, but most cardiovascular deaths in patients with advanced chronic kidney disease are caused by heart failure and sudden cardiac death. While the exact drivers of these deaths are unknown, they are believed to be caused by uremic cardiomyopathy: a specific pattern of myocardial hypertrophy, fibrosis, with both diastolic and systolic dysfunction. Although the pathogenesis of uremic cardiomyopathy is likely to be multifactorial, accumulating evidence suggests increased production of fibroblast growth factor-23 and αKlotho deficiency as potential major drivers of cardiac remodeling in patients with uremic cardiomyopathy. In this article we review the increasing understanding of the physiology and clinical aspects of uremic cardiomyopathy and the rapidly increasing knowledge of the biology of both fibroblast growth factor-23 and αKlotho. Finally, we discuss how dissection of these pathological processes is aiding the development of therapeutic options, including small molecules and antibodies, directly aimed at improving the cardiovascular outcomes of patients with chronic kidney disease and end-stage renal disease.
Keywords: FGF23; cardiorenal syndrome; fibroblast growth factor; growth factor; kidney; treatment; αKlotho.
Figures
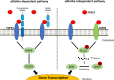
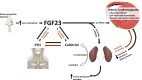
References
-
- Levin A, Tonelli M, Bonventre J, Coresh J, Donner JA, Fogo AB, Fox CS, Gansevoort RT, Heerspink HJL, Jardine M, et al. Global kidney health 2017 and beyond: a roadmap for closing gaps in care, research, and policy. Lancet. 2017;390:1888–1917. - PubMed
-
- Go AS, Chertow GM, Fan D, McCulloch CE, Hsu CY. Chronic kidney disease and the risks of death, cardiovascular events, and hospitalization. N Engl J Med. 2004;351:1296–1305. - PubMed
-
- Chronic Kidney Disease Prognosis C , Matsushita K, van der Velde M, Astor BC, Woodward M, Levey AS, de Jong PE, Coresh J, Gansevoort RT. Association of estimated glomerular filtration rate and albuminuria with all‐cause and cardiovascular mortality in general population cohorts: a collaborative meta‐analysis. Lancet. 2010;375:2073–2081. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

