HPLC-MS/MS Analysis of Aconiti Lateralis Radix Praeparata and Its Combination with Red Ginseng Effect on Rat CYP450 Activities Using the Cocktail Approach
- PMID: 32215046
- PMCID: PMC7085374
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/8603934
HPLC-MS/MS Analysis of Aconiti Lateralis Radix Praeparata and Its Combination with Red Ginseng Effect on Rat CYP450 Activities Using the Cocktail Approach
Abstract
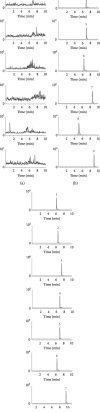
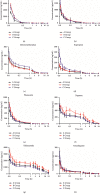
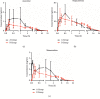
Red ginseng is often combined with Aconiti Lateralis Radix Praeparata to reduce alkaloids-related toxicity of the latter. Such herb-pairing also results in better therapeutic effect in heart failure, as compared to the singular use of either herb. The purpose of this study was to investigate the effect of Aconiti Lateralis Radix Praeparata and its combination with red ginseng on the activities of CYP450 enzymes in rats. A sensitive and reliable HPLC-MS/MS method was established and validated for the simultaneous determination of eight probe drugs, phenacetin (CYP1A2), tolbutamide (CYP2C9), omeprazole (CYP2C19), dextromethorphan (CYP2D6), dapsone (CYP3A4), 7-hydroxycoumarin (CYP2A6), bupropion (CYP2B6), and amodiaquine (CYP2C8), in rat plasma using diazepam as internal standard (IS). The chromatographic separation was performed on a Waters XBridge™ C18 column (2.1 mm × 100 mm, 3.5 μm) using a gradient elution with the mobile phase consisting of acetonitrile and water (containing 0.1% formic acid) at a flow rate of 0.3 mL/min. The method was successfully applied in evaluating the effect of Aconiti Lateralis Radix Praeparata and red ginseng on the activities of CYP450 enzymes. The pharmacokinetic results of the eight probe drugs suggested that Aconiti Lateralis Radix Praeparata may inhibit the activity of CYP2A6, CYP2C19, CYP2B6, CYP1A2, CYP3A4, and CYP2C9 enzymes in rats. Comparison between the two groups, Aconiti Lateralis Radix Praeparata combined with red ginseng and Aconiti Lateralis Radix Praeparata, indicated that red ginseng may inhibit the activity of CYP2D6 and CYP2B6 enzymes while inducing the activity of CYP1A2, CYP3A4, and CYP2C9 enzymes.
Copyright © 2020 Wenjuan Ma et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Liang S. Y., Tan X. M., Gao J., Hu Y. L., Wang W. F. Study on acute toxicity of total alkaloids of processed Radix Aconiti Lateralis and its effects on blood histamine contents and pathomorphological changes in nasal mucosa in allergic rhinitis Guinea pigs. China Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine and Pharmacy. 2011;26(12):2986–2989.
-
- Zhang Y. P., Du G. J., Sun T., Li J. H., Liu W. J., Wang Y. Y. Antitumor effect of total alkaloids from Aconiti Lateralis Radix Praeparata on breast cancer in mice. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs. 2012;43(10):1986–1990.
-
- Wang S. J., Yu H. Y., Ji X. M., Wu Z. C., Han B. B. The influence of aconite root on the expressions of genes related to the metabolism of oxygen free radicals and sex hormones. Chinese Journal of Gerontology. 2012;32(5):961–963.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

