Involvement of HSP90 in ischemic postconditioning-induced cardioprotection by inhibition of the complement system, JNK and inflammation
- PMID: 32215465
- PMCID: PMC7092678
- DOI: 10.1590/s0102-865020200010000005
Involvement of HSP90 in ischemic postconditioning-induced cardioprotection by inhibition of the complement system, JNK and inflammation
Abstract
Purpose: To investigate whether heat shock protein 90 (HSP90) is involved in complement regulation in ischemic postconditioning (IPC).
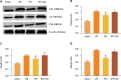
Methods: The left coronary artery of rats underwent 30 min of occlusion, followed by 120 min of reperfusion and treatment with IPC via 3 cycles of 30s reperfusion and 30s occlusion. The rats were injected intraperitoneally with 1 mg/kg HSP90 inhibitor geldanamycin (GA) after anesthesia. Eighty rats were randomly divided into four groups: sham, ischemia-reperfusion (I/R), IPC and IPC + GA. Myocardial infarct size, apoptosis index and the expression of HSP90, C3, C5a, tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha, interleukin (IL)-1β and c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) were assessed.
Results: Compared with the I/R injury, the IPC treatment significantly reduced infarct size, release of troponin T, creatine kinase-MB, and lactate dehydrogenase, and cardiomyocyte apoptosis. These beneficial effects were accompanied by a decrease in TNF-α, IL-1β, C3, C5a and JNK expression levels. However, all these effects were abrogated by administration of the HSP90 inhibitor GA.
Conclusion: HSP90 exerts a profound effect on IPC cardioprotection, and may be linked to the inhibition of the complement system and JNK, ultimately attenuating I/R-induced myocardial injury and apoptosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: none
Figures




References
-
- Hearse DJ, Bolli R. Reperfusion induced injury: manifestations, mechanisms, and clinical relevance. 10.1093/cvr/26.2.101Cardiovasc Res. 1992;26(2):101–108. - PubMed
-
- Timmers L, Pasterkamp G, de Hoog VC, Arslan F, Appelman Y, de Kleijn DP. The innate immune response in reperfused myocardium. 10.1093/cvr/cvs018Cardiovasc Res. 2012;94(2):276–283. - PubMed
-
- Chakraborti T, Mandal A, Mandal M, Das S, Chakraborti S. Complement activation in heart diseases. Role of oxidants. 10.1016/s0898-6568(00)00111-xCell Signal. 2000;12(9-10):607–617. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

