Outcomes of Observation vs Stereotactic Ablative Radiation for Oligometastatic Prostate Cancer: The ORIOLE Phase 2 Randomized Clinical Trial
- PMID: 32215577
- PMCID: PMC7225913
- DOI: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2020.0147
Outcomes of Observation vs Stereotactic Ablative Radiation for Oligometastatic Prostate Cancer: The ORIOLE Phase 2 Randomized Clinical Trial
Abstract
Importance: Complete metastatic ablation of oligometastatic prostate cancer may provide an alternative to early initiation of androgen deprivation therapy (ADT).
Objective: To determine if stereotactic ablative radiotherapy (SABR) improves oncologic outcomes in men with oligometastatic prostate cancer.
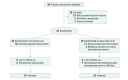
Design, setting, and participants: The Observation vs Stereotactic Ablative Radiation for Oligometastatic Prostate Cancer (ORIOLE) phase 2 randomized study accrued participants from 3 US radiation treatment facilities affiliated with a university hospital from May 2016 to March 2018 with a data cutoff date of May 20, 2019, for analysis. Of 80 men screened, 54 men with recurrent hormone-sensitive prostate cancer and 1 to 3 metastases detectable by conventional imaging who had not received ADT within 6 months of enrollment or 3 or more years total were randomized.
Interventions: Patients were randomized in a 2:1 ratio to receive SABR or observation.
Main outcomes and measures: The primary outcome was progression at 6 months by prostate-specific antigen level increase, progression detected by conventional imaging, symptomatic progression, ADT initiation for any reason, or death. Predefined secondary outcomes were toxic effects of SABR, local control at 6 months with SABR, progression-free survival, Brief Pain Inventory (Short Form)-measured quality of life, and concordance between conventional imaging and prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA)-targeted positron emission tomography in the identification of metastatic disease.
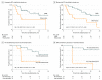
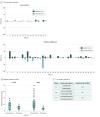
Results: In the 54 men randomized, the median (range) age was 68 (61-70) years for patients allocated to SABR and 68 (64-76) years for those allocated to observation. Progression at 6 months occurred in 7 of 36 patients (19%) receiving SABR and 11 of 18 patients (61%) undergoing observation (P = .005). Treatment with SABR improved median progression-free survival (not reached vs 5.8 months; hazard ratio, 0.30; 95% CI, 0.11-0.81; P = .002). Total consolidation of PSMA radiotracer-avid disease decreased the risk of new lesions at 6 months (16% vs 63%; P = .006). No toxic effects of grade 3 or greater were observed. T-cell receptor sequencing identified significant increased clonotypic expansion following SABR and correlation between baseline clonality and progression with SABR only (0.082085 vs 0.026051; P = .03).
Conclusions and relevance: Treatment with SABR for oligometastatic prostate cancer improved outcomes and was enhanced by total consolidation of disease identified by PSMA-targeted positron emission tomography. SABR induced a systemic immune response, and baseline immune phenotype and tumor mutation status may predict the benefit from SABR. These results underline the importance of prospective randomized investigation of the oligometastatic state with integrated imaging and biological correlates.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT02680587.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Comment in
-
Forging New Strategies in the Cure of Human Oligometastatic Cancer.JAMA Oncol. 2020 May 1;6(5):659-660. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2020.0195. JAMA Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32215582 No abstract available.
-
SABR improves outcomes in men with recurrent oligometastatic prostate cancer.Nat Rev Urol. 2020 May;17(5):256. doi: 10.1038/s41585-020-0321-0. Nat Rev Urol. 2020. PMID: 32313111 No abstract available.
-
Oral ADT demonstrates greater efficacy than existing injectable treatment.Nat Rev Urol. 2020 May;17(5):256. doi: 10.1038/s41585-020-0322-z. Nat Rev Urol. 2020. PMID: 32313112 No abstract available.
-
Flattening the Curve of Prostate Cancer Progression: Accurate Detection and Safe Ablation.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2020 Jul 15;107(4):609-612. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2020.04.028. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2020. PMID: 32589984 No abstract available.
-
Metastasis-Directed Therapy for Oligorecurrent Prostate Cancer-Not All That Glitters Is Gold-Reply.JAMA Oncol. 2020 Oct 1;6(10):1639. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2020.2842. JAMA Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32815993 No abstract available.
-
Metastasis-Directed Therapy for Oligorecurrent Prostate Cancer-Not All That Glitters Is Gold.JAMA Oncol. 2020 Oct 1;6(10):1638-1639. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2020.2829. JAMA Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32815997 No abstract available.
-
Stereotaktische ablative Radiatio beim oligometastasierten Prostatakarzinom.Aktuelle Urol. 2021 Feb;52(1):22. doi: 10.1055/a-1170-9469. Epub 2021 Feb 1. Aktuelle Urol. 2021. PMID: 33525023 German. No abstract available.
-
Re: Outcomes of Observation vs Stereotactic Ablative Radiation for Oligometastatic Prostate Cancer: The ORIOLE Phase 2 Randomized Clinical Trial.Eur Urol. 2021 Jun;79(6):889-890. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2021.02.011. Epub 2021 Feb 23. Eur Urol. 2021. PMID: 33632550 No abstract available.
-
Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy for Oligometastasis: GUst Do It?Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2022 Nov 15;114(4):561-570. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2022.07.026. Epub 2022 Oct 13. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2022. PMID: 36244387 No abstract available.
References
-
- Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program Cancer stat facts: prostate cancer. Accessed January 28, 2020. https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/prost.html
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

