Effects of aging on the quality of roasted sesame-like flavor Daqu
- PMID: 32216749
- PMCID: PMC7098102
- DOI: 10.1186/s12866-020-01745-3
Effects of aging on the quality of roasted sesame-like flavor Daqu
Abstract
Background: Daqu, the saccharification, fermentation, and aroma-producing agents for Baijiu brewing, is prepared using a complex process. Aging is important for improving the quality of Daqu, but its impact has rarely been studied. This study investigated changes in the physicochemical properties, flavor compounds, and microbial communities during aging of Daqu with a roasted sesame-like flavor.
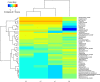
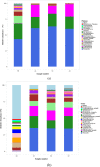
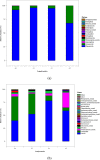
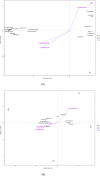
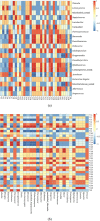
Results: The physicochemical properties changed continuously during aging to provide a high esterifying activity. Aging removed unpleasant flavor compounds and helped to stabilize the flavor compounds in mature Daqu. A high-throughput sequencing approach was used to analyze the changing composition of the microbial communities during aging. Aging helped to modify the microbial population to produce better Baijiu by eliminating low-abundance microbial communities and optimizing the proportion of predominant microbial communities. Nine genera of prokaryotic microbes formed the core microbiota in Daqu after aging. Regarding eukaryotic microbes, Zygomycota, the predominant community, increased in the first 2 months, then decreased in the third month of aging, while Ascomycota, the subdominant community, showed the opposite behavior. Absidia, Trichocomaceae_norank and Rhizopus were the predominant genera in the mature Daqu.
Conclusions: Significant correlations between microbiota and physicochemical properties or flavor compounds were observed, indicating that optimizing microbial communities is essential for aging Daqu. This study provides detailed information on aging during Daqu preparation.
Keywords: Baijiu; Esterifying activity; Eukaryotic microbes; High-throughput sequencing; Prokaryotic microbes; Volatile compounds.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Pang XN, Han BZ, Huang XN, Zhang X, Hou LF, Cao M, Gao LJ, Hu GH, Chen JY. Effect of the environment microbiota on the flavour of light-flavour Baijiu during spontaneous fermentation. Sci Rep. 2018; 8(3396): http://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-21814-y. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Liu HL, Sun BG. Effect of fermentation processing on the flavor of baijiu. J Agr Food Chem. 2018;66(22):5425–5432. - PubMed
-
- Wang XD, Ban SD, Qiu SY. Analysis of the mould microbiome and exogenous enzyme production in Moutai-flavor Daqu. J I Brewing. 2018;124(1):91–99.
-
- Wang P, Wu Q, Jiang XJ, Wang ZQ, Tang JL, Xu Y. Bacillus licheniformis affects the microbial community and metabolic profile in the spontaneous fermentation of Daqu starter for Chinese liquor making. Int J Food Microbiol. 2017;250:59–67. - PubMed
-
- Ming HM, Zhou J, Zhu LL, Xu DF, Liu YH, Yao X. A comparative study of traditional/new daqu quality indicators system. Liquor-Making Sci Technol. 2015;4:32–36.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

