Multitarget Anticancer Agents Based on Histone Deacetylase and Protein Kinase CK2 inhibitors
- PMID: 32218358
- PMCID: PMC7180456
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules25071497
Multitarget Anticancer Agents Based on Histone Deacetylase and Protein Kinase CK2 inhibitors
Abstract
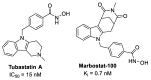
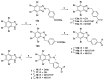
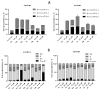
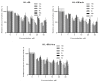
The design of multitarget drugs (MTDs) has become an innovative approach for the search of effective treatments in complex diseases such as cancer. In this work, we communicate our efforts in the design of multi-targeting histone deacetylase (HDAC) and protein kinase CK2 inhibitors as a novel therapeutic strategy against cancer. Using tetrabromobenzotriazole (TBB) and 2-dimethylamino-4,5,6,7-tetrabromo-benzimidazole (DMAT) as scaffolds for CK2 inhibition, and a hydroxamate to coordinate the zinc atom present in the active site of HDAC (zinc binding group, ZBG), new multitarget inhibitors have been designed and synthesized. According to the in vitro assays, N-Hydroxy-6-(4,5,6,7-tetrabromo-2-(dimethylamino)-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-1-yl)hexanamide (11b) is the most interesting compound, with IC50 values of 0.66; 1.46 and 3.67 µM. for HDAC6; HDAC1 and CK2; respectively. Cellular assays on different cancer cell lines rendered promising results for N-Hydroxy-8-(4,5,6,7-tetrabromo-2-(dimethylamino)-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-1-yl)octanamide (11d). This inhibitor presented the highest cytotoxic activity, proapoptotic capability, and the best mitochondria-targeting and multidrug-circumventing properties, thus being the most promising drug candidate for further in vivo studies.
Keywords: CK2; CuAAC; HDAC; cytotoxic activity; docking; molecular dynamics; multi-target inhibitors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures








References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

