A systematic review on different models of inducing obesity in animals: Advantages and limitations
- PMID: 32219116
- PMCID: PMC7096124
- DOI: 10.5455/javar.2020.g399
A systematic review on different models of inducing obesity in animals: Advantages and limitations
Abstract
Several animals have been in the limelight of basic research associated with metabolic diseases like obesity. Obesity can be considered as a significant public health concern in the world. It raises the chances for a variety of disease conditions that includes diabetes, hypertension, liver disease, and cancers, which, in turn, decreases the overall lifespan of adult men and women. The World Health Organization has considered obesity as a global epidemic. Researchers have made several attempts to classify human obesity, but none have been successful. Animal obesity can be classified based on their etiology; however, till now, no animal model of obesity can replicate models of the human condition, they have only provided clues into the causes, aftermaths, and preventive remedy to human adiposity. Over the years, there are varieties of animal models used to induce obesity. Some of them include monogenic, polygenic, surgical, seasonal, and other models of obesity. Apart from the advantages of these models, most of them are accompanied by limitations. The primary purpose of this review is, therefore, to highlight the several models with their advantages and limitations. By knowing the benefits and limitations of animal models of obesity, researchers may be at liberty to select the appropriate one for the study of obesity.
Keywords: Advantages; limitations; monogenicmodel; obesity; polygenic model; surgical model.
Copyright: © Journal of Advanced Veterinary and Animal Research.
Figures
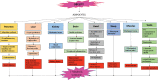
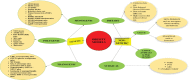
References
-
- Rosso C, Mezzabotta L, Gaggini M, Salomone F, Gambino R, Marengo A, et al. Peripheral insulin resistance predicts liver damage in nondiabetic subjects with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology. 2016;63(1):107–16. https//doi.org/10.1002/hep.28287. - PubMed
-
- Lee S, Paz-Filho G, Mastronardi C, Licinio J, Wong ML. Is increased antidepressant exposure a contributory factor to the obesity pandemic? Transl Psychiat. 2017;6(3):e759. https//doi.org/10.1038/tp.2016.25. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Deurenberg P, Yap M, Van Staveren WA. Body mass index and percent body fat: a meta analysis among different ethnic groups. Int J Obes. 1998;22(12):1164. https//doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0800741. - PubMed
-
- Suleiman JB, Eze ED, Karimah MR, Iliya E. Assessment of body weight, body mass index and waist-hip ratio on academic performance of female students in Akanu Ibiam federal polytechnic unwana, Afikpo, Ebonyi State, Nigeria. Int J Brain Cognit Sci. 2017;6(4):65–70. https://doi:10.5923/j.ijbcs.20170604.01.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
