Accumulation of high-value bioproducts in planta can improve the economics of advanced biofuels
- PMID: 32220956
- PMCID: PMC7165473
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2000053117
Accumulation of high-value bioproducts in planta can improve the economics of advanced biofuels
Erratum in
-
Correction for Yang et al., Accumulation of high-value bioproducts in planta can improve the economics of advanced biofuels.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Oct 27;117(43):27061. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2018562117. Epub 2020 Oct 12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 33046641 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
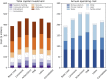
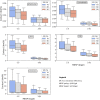
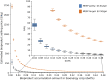
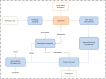
Coproduction of high-value bioproducts at biorefineries is a key factor in making biofuels more cost-competitive. One strategy for generating coproducts is to directly engineer bioenergy crops to accumulate bioproducts in planta that can be fractionated and recovered at biorefineries. Here, we develop quantitative insights into the relationship between bioproduct market value and target accumulation rates by investigating a set of industrially relevant compounds already extracted from plant sources with a wide range of market prices and applications, including <$10/kg (limonene, latex, and polyhydroxybutyrate [PHB]), $10 to $100/kg (cannabidiol), and >$100/kg (artemisinin). These compounds are used to identify a range of mass fraction thresholds required to achieve net economic benefits for biorefineries and the additional amounts needed to reach a target $2.50/gal biofuel selling price, using cellulosic ethanol production as a test case. Bioproduct market prices and recovery costs determine the accumulation threshold; we find that moderate- to high-value compounds (i.e., cannabidiol and artemisinin) offer net economic benefits at accumulation rates of just 0.01% dry weight (dwt) to 0.02 dwt%. Lower-value compounds, including limonene, latex, and PHB, require at least an order-of-magnitude greater accumulation to overcome additional extraction and recovery costs (0.3 to 1.2 dwt%). We also find that a diversified approach is critical. For example, global artemisinin demand could be met with fewer than 10 biorefineries, while global demand for latex is equivalent to nearly 180 facilities. Our results provide a roadmap for future plant metabolic engineering efforts aimed at increasing the value derived from bioenergy crops.
Keywords: bioenergy crop; biofuel; bioproduct; in planta accumulation; technoeconomic analysis.
Copyright © 2020 the Author(s). Published by PNAS.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures


References
-
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency , Regulation of Fuels and Fuel Additives: Changes to Renewable Fuel Standard Program (U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, 2010).
-
- Baral N. R., et al. , Techno-economic analysis and life-cycle greenhouse gas mitigation cost of five routes to bio-jet fuel blendstocks. Energy Environ. Sci. 12, 807–824 (2019).
-
- Budzianowski W. M., High-value low-volume bioproducts coupled to bioenergies with potential to enhance business development of sustainable biorefineries. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 70, 793–804 (2017).
-
- Baral N. R., et al. , Approaches for more efficient biological conversion of lignocellulosic feedstocks to biofuels and bioproducts. ACS Sustain. Chem.& Eng. 7, 9062–9079 (2019).
-
- Bioenergy Technology Office , Strategic Plan. For a Thriving and Sustainable Bioeconomy (US Department of Energy, 2016).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

