Antihyperthermic treatment decreases perihematomal hypodensity
- PMID: 32221027
- PMCID: PMC7282877
- DOI: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000009288
Antihyperthermic treatment decreases perihematomal hypodensity
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the effect on perihematomal hypodensity and outcome of a decrease in body temperature in the first 24 hours in patients with intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH).
Methods: In this retrospective study on a prospectively registered database, among the 1,100 patients, 795 met all the inclusion criteria. Temperature variations in the first 24 hours and perihematomal hypodensity (PHHD) were recorded. Patients ≥37.5°C were treated with antihyperthermic drugs for at least 48 hours. The main objective was to determine the association among temperature variation, PHHD, and outcome at 3 months.
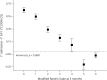
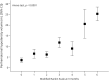
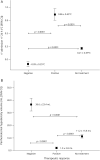
Results: The decrease in temperature in the first 24 hours increased the possibility of good outcome 11-fold. Temperature decrease, lower PHHD volume, and a good outcome were observed in 31.8% of the patients who received antihyperthermic treatment.
Conclusion: The administration of early antihyperthermic treatment in patients with spontaneous ICH with a basal axillary temperature ≥37.5°C resulted in good outcome in a third of the treated patients.
Copyright © 2020 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of the American Academy of Neurology.
Figures


Comment in
-
Hyperthermia, cerebral edema, and outcome in intracerebral hemorrhage: Too darn hot.Neurology. 2020 Apr 21;94(16):687-688. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000009284. Epub 2020 Mar 27. Neurology. 2020. PMID: 32221029 No abstract available.
References
-
- Tuhrim S, Horowitz DR, Scacher M, et al. . Comparison of model predicting survival following intracerebral hemorrhage. Crit Care Med 1995;23:950–954. - PubMed
-
- Leira R, Dávalos A, Silva Y, et al. . Early neurologic deterioration in intracerebral hemorrhage: predictors and associated factors. Neurology 2004;63:461–467. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
