Atypical Development of Attentional Control Associates with Later Adaptive Functioning, Autism and ADHD Traits
- PMID: 32221749
- PMCID: PMC7557503
- DOI: 10.1007/s10803-020-04465-9
Atypical Development of Attentional Control Associates with Later Adaptive Functioning, Autism and ADHD Traits
Abstract
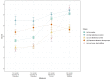
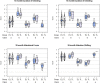
Autism is frequently associated with difficulties with top-down attentional control, which impact on individuals' mental health and quality of life. The developmental processes involved in these attentional difficulties are not well understood. Using a data-driven approach, 2 samples (N = 294 and 412) of infants at elevated and typical likelihood of autism were grouped according to profiles of parent report of attention at 10, 15 and 25 months. In contrast to the normative profile of increases in attentional control scores between infancy and toddlerhood, a minority (7-9%) showed plateauing attentional control scores between 10 and 25 months. Consistent with pre-registered hypotheses, plateaued growth of attentional control was associated with elevated autism and ADHD traits, and lower adaptive functioning at age 3 years.
Keywords: ADHD; Attention; Atypical development; Autism; Infant; Intermediate phenotype.
Conflict of interest statement
Bölte discloses that he has in the last 5 years acted as an author, consultant or lecturer for Shire/Takeda, Medice, Roche, Eli Lilly, Prima Psychiatry, and SB Education and Psychological Consulting AB. He receives royalties for text books and diagnostic tools from Huber/Hogrefe, Kohlhammer and UTB. Charman discloses that he has served as a consultant to F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd and has received royalties from Sage Publications and Guilford Publications. All other authors report no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Achenbach TM, Rescorla LA. Manual for the ASEBA school-age forms & profiles. Burlington, VT: University of Vermont, Research Center for Children, Youth, & Families; 2001.
-
- Adamek L, Nichols S, Tetenbaum SP, Bregman J, Ponzio CA, Carr EG. Individual temperament and problem behavior in children with autism spectrum disorders. Focus on Autism and Other Developmental Disabilities. 2011;26(3):173–183. doi: 10.1177/1088357611405041. - DOI
-
- APA . Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. 5. Washington, DC: APA; 2013.
-
- Asparouhov T, Muthen B. Auxiliary variables in mixture modeling: Three-step approaches using mplus. Structural Equation Modeling-a Multidisciplinary Journal. 2014;21(3):329–341. doi: 10.1080/10705511.2014.915181. - DOI
-
- Baio J, Wiggins L, Christensen DL, Maenner MJ, Daniels J, Warren Z, et al. Prevalence of autism spectrum disorder among children aged 8 years—autism and developmental disabilities monitoring network, 11 sites, United States, 2014. MMWR Surveillance Summaries. 2018;67(6):1. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.ss6706a1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

