Bumped Kinase Inhibitors as therapy for apicomplexan parasitic diseases: lessons learned
- PMID: 32224121
- PMCID: PMC8565993
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijpara.2020.01.006
Bumped Kinase Inhibitors as therapy for apicomplexan parasitic diseases: lessons learned
Abstract
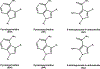
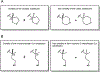
Bumped Kinase Inhibitors, targeting Calcium-dependent Protein Kinase 1 in apicomplexan parasites with a glycine gatekeeper, are promising new therapeutics for apicomplexan diseases. Here we will review advances, as well as challenges and lessons learned regarding efficacy, safety, and pharmacology that have shaped our selection of pre-clinical candidates.
Keywords: Apicomplexa; Bumped Kinase Inhibitor; Calcium-dependent Protein Kinases; Cryptosporidium; Gatekeeper; Neospora; Sarcocystis; Toxoplasma.
Copyright © 2020. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Arnold SLM, Choi R, Hulverson MA, Schaefer DA, Vinayak S, Vidadala RSR, McCloskey MC, Whitman GR, Huang W, Barrett LK, Ojo KK, Fan E, Maly DJ, Riggs MW, Striepen B, Van Voorhis WC, 2017. Necessity of Bumped Kinase Inhibitor Gastrointestinal Exposure in Treating Cryptosporidium Infection. J Infect Dis 216, 55–63. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Arnold SLM, Choi R, Hulverson MA, Whitman GR, McCloskey MC, Dorr CS, Vidadala RSR, Khatod M, Morada M, Barrett LK, Maly DJ, Yarlett N, Van Voorhis WC, 2019. P-glycoprotein mediated efflux reduces the in vivo efficacy of a therapeutic targeting the gastrointestinal parasite Cryptosporidium. J Infect Dis 220, 1188–1198. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chen J, Deng F, Singh SV, Wang QJ, 2008. Protein kinase D3 (PKD3) contributes to prostate cancer cell growth and survival through a PKCepsilon/PKD3 pathway downstream of Akt and ERK 1/2. Cancer Res 68, 3844–3853. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

