Luteolin-7-O-Glucoside Inhibits Oral Cancer Cell Migration and Invasion by Regulating Matrix Metalloproteinase-2 Expression and Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase Pathway
- PMID: 32224968
- PMCID: PMC7226481
- DOI: 10.3390/biom10040502
Luteolin-7-O-Glucoside Inhibits Oral Cancer Cell Migration and Invasion by Regulating Matrix Metalloproteinase-2 Expression and Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase Pathway
Abstract
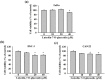
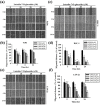
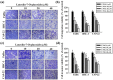
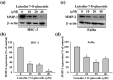
Oral squamous cell carcinoma is the sixth most common type of cancer globally, which is associated with high rates of cancer-related deaths. Metastasis to distant organs is the main reason behind worst prognostic outcome of oral cancer. In the present study, we aimed at evaluating the effects of a natural plant flavonoid, luteolin-7-O-glucoside, on oral cancer cell migration and invasion. The study findings showed that in addition to preventing cell proliferation, luteolin-7-O-glucoside caused a significant reduction in oral cancer cell migration and invasion. Mechanistically, luteolin-7-O-glucoside caused a reduction in cancer metastasis by reducing p38 phosphorylation and downregulating matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-2 expression. Using a p38 inhibitor, SB203580, we proved that luteolin-7-O-glucoside exerts anti-migratory effects by suppressing p38-mediated increased expression of MMP-2. This is the first study to demonstrate the luteolin-7-O-glucoside inhibits cell migration and invasion by regulating MMP-2 expression and extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathway in human oral cancer cell. The study identifies luteolin-7-O-glucoside as a potential anti-cancer candidate that can be utilized clinically for improving oral cancer prognosis.
Keywords: Luteolin-7-O-glucoside; MMP-2; invasion; migration; oral cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
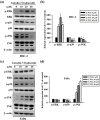
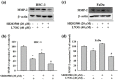
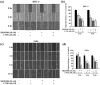
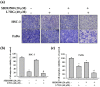
References
-
- Smriti K., Ray M., Chatterjee T., Shenoy R.-P., Gadicherla S., Pentapati K.-C., Rustaqi N. Salivary MMP-9 as a Biomarker for the Diagnosis of Oral Potentially Malignant Disorders and Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2020;21:233–238. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2020.21.1.233. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Su S.-C., Lin C.-W., Liu Y.-F., Fan W.-L., Chen M.-K., Yu C.-P., Yang W.-E., Su C.-W., Chuang C.-Y., Li W.-H., et al. Exome Sequencing of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Reveals Molecular Subgroups and Novel Therapeutic Opportunities. Theranostics. 2017;7:1088–1099. doi: 10.7150/thno.18551. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Haigentz M., Jr., Hartl D.M., Silver C.E., Langendijk J.A., Strojan P., Paleri V., De Bree R., Machiels J.P., Hamoir M., Rinaldo A., et al. Distant metastases from head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Part III. Treatment. Oral Oncol. 2012;48:787–793. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2012.03.019. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Takes R.P., Rinaldo A., Silver C.E., Haigentz M., Jr., Woolgar J.A., Triantafyllou A., Mondin V., Paccagnella D., De Bree R., Shaha A.R., et al. Distant metastases from head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Part I. Basic aspects. Oral Oncol. 2012;48:775–779. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2012.03.013. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

