CSN6-TRIM21 axis instigates cancer stemness during tumorigenesis
- PMID: 32225170
- PMCID: PMC7250844
- DOI: 10.1038/s41416-020-0779-9
CSN6-TRIM21 axis instigates cancer stemness during tumorigenesis
Erratum in
-
Correction: CSN6-TRIM21 axis instigates cancer stemness during tumorigenesis.Br J Cancer. 2020 Sep;123(6):1042-1044. doi: 10.1038/s41416-020-0977-5. Br J Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32647365 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: Cancer stem cells (CSCs) are responsible for tumour initiation, metastasis and recurrence. However, the mechanism of CSC formation, maintenance and expansion in colorectal cancer (CRC) remains poorly characterised.
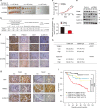
Methods: The role of COP9 signalosome subunit 6 (CSN6) in regulating cancer stemness was evaluated by organoid formation and limited dilution analysis. The role of CSN6-TRIM21-OCT1-ALDH1A1 axis in CSC formation was evaluated in vitro and in vivo. The association of CSN6, TRIM21 and ALDH1A1 expression was validated by a tissue microarray with 267 CRC patients.
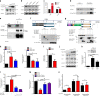
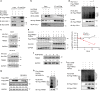
Results: The results showed that CSN6 is critical for sphere formation and maintaining the growth of patient-derived organoids (PDOs). We characterised the role of CSN6 in regulating cancer stemness, which involves the TRIM21 E3 ubiquitin ligase, transcription factor POU class 2 homeobox 1 (OCT1) and cancer stem cell marker aldehyde dehydrogenase 1 A1 (ALDH1A1). Our data showed that CSN6 facilitates ubiquitin-mediated degradation of TRIM21, which in turn decreases TRIM21-mediated OCT1 ubiquitination and subsequently stabilises OCT1. Consequently, OCT1 stabilisation leads to ALDH1A1expression and promotes cancer stemness. We further showed that the protein expression levels of CSN6, TRIM21 and ALDH1A1 can serve as prognostic markers for human CRC.
Conclusions: In conclusion, we validate a pathway for cancer stemness regulation involving ALDH1A1 levels through the CSN6-TRIM21 axis, which may be utilised as CRC molecular markers and be targeted for therapeutic intervention in cancers.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Brenner H, Kloor M, Pox CP. Colorectal cancer. Lancet. 2014;383:1490–1502. - PubMed
-
- Henderson K, Kirkland SC. Multilineage differentiation of cloned HRA-19 cells in serum-free medium: a model of human colorectal epithelial differentiation. Differentiation. 1996;60:259–268. - PubMed
-
- Vermeulen L, Snippert HJ. Stem cell dynamics in homeostasis and cancer of the intestine. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2014;14:468–480. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

