Sophorolipid Biosurfactant Can Control Cutaneous Dermatophytosis Caused by Trichophyton mentagrophytes
- PMID: 32226417
- PMCID: PMC7080852
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.00329
Sophorolipid Biosurfactant Can Control Cutaneous Dermatophytosis Caused by Trichophyton mentagrophytes
Abstract
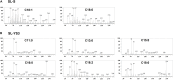
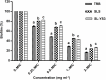
Trichophyton mentagrophytes, a zoophilic species, is one of the most frequently isolated dermatophytes in many parts of the world. This study investigated the efficacy of a sophorolipid (SL-YS3) produced by Rhodotorula babjevae YS3 against dermatophytosis caused by T. mentagrophytes. SL-YS3 was characterized by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) and ultra-performance liquid chromatography, coupled with electrospray mass spectrometry (UPLC-ESI-MS). SL-YS3 comprised of six different fatty acids as the hydrophobic components of constituent congeners and sophorose as the hydrophilic component. Inhibitory effects of purified SL-YS3 against hyphal growth was found to be 85% at a 2 mg ml-1 concentration, and MIC was 1 mg ml-1. Microscopic examination with scanning electron microscopy (SEM), atomic force microscopy, and confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM) revealed that SL-YS3 exerts its effect by disrupting cell membrane integrity causing cell death. SL-YS3 was also effective in reducing the biofilms formed by T. mentagrophytes, which was observed spectrophotometrically with crystal-violet staining and further validated with SEM and CLSM studies of treated biofilms. In vivo studies in a mouse model of cutaneous dermatophytosis involving macroscopic observations, percent culture recovery from skin samples, and histopathological studies showed that SL-YS3 could effectively cure the infected mice after 21 days of topical treatment. Terbinafine (TRB) was used as a standard drug in the experiments. We demonstrate, for the first time, the antidermatophytic activity of a sophorolipid biosurfactant. The findings are suggestive that SL-YS3 can be formulated as a novel antifungal compound to treat cutaneous mycoses caused by T. mentagrophytes.
Keywords: Trichophyton mentagrophytes; antibiofilm activity; biosurfactant; dermatophytosis; sophorolipid; topical application; ultramicroscopy.
Copyright © 2020 Sen, Borah, Kandimalla, Bora and Deka.
Figures








References
-
- Almeida D. D. F., Fraga-Silva T. F., Santos A. R., Finato A. C., Marchetti C. M., Golim M. D. A, et al. (2017). TLR2-/- mice display increased clearance of dermatophyte Trichophyton mentagrophytes in the setting of hyperglycemia. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 7:8. 10.3389/fcimb.2017.00008 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

