Internal exposure to perfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) and biological markers in 101 healthy 1-year-old children: associations between levels of perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) and vaccine response
- PMID: 32227269
- PMCID: PMC7303054
- DOI: 10.1007/s00204-020-02715-4
Internal exposure to perfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) and biological markers in 101 healthy 1-year-old children: associations between levels of perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) and vaccine response
Abstract
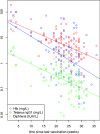
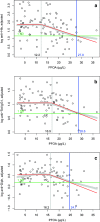
Perfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) are a complex group of man-made chemicals with high stability and mobility leading to ubiquitous environmental contamination and accumulation in the food chain. In human serum/plasma samples, perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) and perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) are the lead compounds. They are immunotoxic in experimental animals, and epidemiological studies provided evidence of a diminished production of vaccine antibodies in young children. However, information on children of the first year of age is missing but relevant, as they have a relatively high exposure if breastfed, and may have a higher susceptibility as their immune system is developing. In a cross-sectional study with 101 healthy 1-year-old children, internal levels of persistent organic pollutants and a broad panel of biological parameters were investigated at the end of the 1990s. Additional analysis of PFASs resulted in plasma levels (mean ± SD) of PFOA and PFOS of 3.8 ± 1.1 and 6.8 ± 3.4 µg/L, respectively, in the 21 formula-fed children, and of 16.8 ± 6.6 and 15.2 ± 6.9 µg/L in the 80 children exclusively breastfed for at least 4 months. The study revealed significant associations between levels of PFOA, but not of PFOS, and adjusted levels of vaccine antibodies against Haemophilus influenza type b (Hib, r = 0.32), tetanus (r = 0.25) and diphtheria (r = 0.23), with no observed adverse effect concentrations (NOAECs) determined by fitting a 'knee' function of 12.2, 16.9 and 16.2 µg/L, respectively. The effect size (means for PFOA quintiles Q1 vs. Q5) was quantified to be - 86, - 54 and - 53%, respectively. Furthermore, levels of PFOA were inversely associated with the interferon gamma (IFNɣ) production of ex-vivo lymphocytes after stimulation with tetanus and diphtheria toxoid, with an effect size of - 64 and - 59% (means Q1 vs. Q5), respectively. The study revealed no influence of PFOA and PFOS on infections during the first year of life and on levels of cholesterol. Our results confirmed the negative associations of PFAS levels and parameters of immune response observed in other epidemiological studies, with high consistency as well as comparable NOAECs and effects sizes for the three vaccine antibodies investigated, but for PFOA only. Due to reduction of background levels of PFASs during the last 20 years, children in Germany nowadays breastfed for a long duration are for the most part not expected to reach PFOA levels at the end of the breastfeeding period above the NOAECs determined.
Keywords: Children; Cholesterol; Immune response; Perfluoroalkyl substances; Vaccine antibodies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Abraham K (2000) Belastung von Säuglingen mit polychlorierten Dibenzo-p-dioxinen (PCDDs), Dibenzofuranen (PCDFs) und Biphenylen (PCBs) und deren Auswirkung auf sensible biologische Parameter, Abschlußbericht des Projektes PUG U 96 005. In: Abraham K (ed.) Exposition gegenüber Dioxinen und verwandten Substanzen – ein Risiko für Säuglinge? Habilitationsschrift Charité. https://edoc.hu-berlin.de/handle/18452/14507. Accessed 15 Jan 2020
-
- Abraham K, Müller C, Grüters A, Wahn U, Schweigert FJ. Minimal inflammation, acute phase response and avoidance of misclassification of vitamin A and iron status in infants—importance of a high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (CRP) assay. Int J Vitam Nutr Res. 2003;73:423–430. doi: 10.1024/0300-9831.73.6.423. - DOI - PubMed
-
- ATSDR, Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2018) Toxicological profile for Perfluoroalkyls (Draft for Public Comment). U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Public Health Service, Atlanta. https://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/toxprofiles/tp200.pdf. Accessed 15 Jan 2020
-
- Benemann J, Bromen K, Lehmann N, Marr A, Jöckel KH (2004) Umwelt-Survey 1998 Band VII: Arsen, Schwer- und Edelmetalle in Blut und Urin der Bevölkerung in Deutschland – Belastungsquellen und -pfade. German Environment Agency. https://www.umweltbundesamt.de/publikationen/umwelt-survey-1998-4. Accessed 15 Jan 2020
-
- C8 Science Panel (2012) Probable link evaluation of infectious disease. https://www.c8sciencepanel.org/pdfs/Probable_Link_C8_Infections_30Jul201...
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

