The correlation between viral clearance and biochemical outcomes of 94 COVID-19 infected discharged patients
- PMID: 32227274
- PMCID: PMC7103893
- DOI: 10.1007/s00011-020-01342-0
The correlation between viral clearance and biochemical outcomes of 94 COVID-19 infected discharged patients
Abstract
Objective: This study aims to evaluate the correlation between viral clearance and blood biochemical index of 94 discharged patients with COVID-19 infection in Shenzhen Third People's Hospital, enrolled from Jan 5 to Feb 13, 2020.
Methods: The clinical and laboratory findings were extracted from the electronic medical records of the patients. The data were analysed and reviewed by a trained team of physicians. Information on clinical signs and symptoms, medical treatment, virus clearance, and laboratory parameters including interleukin 6 (IL-6) and C-reactive protein were collected.
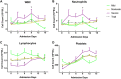
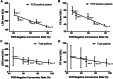
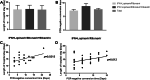
Results: COVID-19 mRNA clearance ratio was identified significantly correlated with the decline of serum creatine kinase (CK) and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) levels. Furthermore, COVID-19 mRNA clearance time was positively correlated with the length of hospital stay in patients treated with either IFN-α + lopinavir/ritonavir or IFN-α + lopinavir/ritonavir + ribavirin.
Conclusions: Therapeutic regimens of IFN-α + lopinavir/ritonavir and IFN-α + lopinavir/ritonavir + ribavirin might be beneficial for treatment of COVID-19. Serum LDH or CK decline may predict a favorable response to treatment of COVID-19 infection.
Keywords: CK; COVID-19; Clearance ratio; LDH.
Conflict of interest statement
The findings and conclusions are those of the authors and do not necessarily represent the views of the Shenzhen Third People's Hospital. All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest exists.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

