Sitagliptin affects gastric cancer cells proliferation by suppressing Melanoma-associated antigen-A3 expression through Yes-associated protein inactivation
- PMID: 32227453
- PMCID: PMC7286447
- DOI: 10.1002/cam4.3024
Sitagliptin affects gastric cancer cells proliferation by suppressing Melanoma-associated antigen-A3 expression through Yes-associated protein inactivation
Abstract
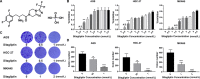
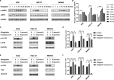
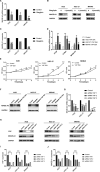
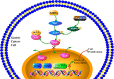
Sitagliptin is an emerging oral hypoglycemic agent that inhibits the development of a wide variety of tumors. Current researches indicate that the abnormal activation of Yes-associated protein (YAP) promotes the proliferation and poor prognosis of multiple tumors. However, the ability of sitagliptin to regulate YAP and its effects on gastric cancer (GC) cells remain unclear. Here, we first showed that sitagliptin inhibited the proliferation of GC cells, and this inhibition was regulated by Hippo pathway. Sitagliptin phosphorylated YAP in a large tumor suppressor homolog-dependent manner, thereby inhibiting YAP nuclear translocation, and promoted YAP cytoplasm retention. This inhibition can be blocked by adenosine 5'-monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK). Moreover, sitagliptin could reduce the expression of tumor-testis antigen Melanoma-associated antigen-A3 through YAP. In conclusion, sitagliptin may have a potential inhibitory effect on GC by AMPK/YAP/melanoma-associated antigen-A3 pathway.
Keywords: MAGE-A3; YAP; gastric cancer; sitagliptin.
© 2020 The Authors. Cancer Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures


References
-
- Ogurtsova K, da Rocha Fernandes JD, Huang Y, et al. IDF Diabetes Atlas: global estimates for the prevalence of diabetes for 2015 and 2040. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2017;128:40‐50. - PubMed
-
- Prakash S, Rai U, Kosuru R, Tiwari V, Singh SJB. Amelioration of diet‐induced metabolic syndrome and fatty liver with Sitagliptin via regulation of adipose tissue inflammation and hepatic Adiponectin/AMPK levels in mice. Biochimie. 2020;168:198‐209. - PubMed
-
- Tseng CH. Sitagliptin may reduce breast cancer risk in women with type 2 diabetes. Clin Breast Cancer. 2017;17(3):211‐218. - PubMed
-
- Kabel AM, Atef A, Estfanous RS. Ameliorative potential of sitagliptin and/or resveratrol on experimentally‐induced clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;97:667‐674. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

